Summary
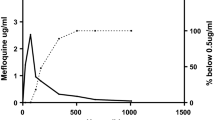
Mefloquine, a quinolinemethanol antimalarial, is effective single dose therapy for all species of malaria infecting humans, including multi-drug—resistant Plasmodium falciparum. It is used both in prophylaxis and treatment. Mefloquine is available either as the hydrochloride salt alone, or in a combined preparation with sulfadoxine and pyrimethamine. There is no parenteral formulation. Several assay methodologies have been developed, but high performance liquid chromatography has been the most used in recent pharmacokinetic studies. These have shown in healthy volunteers that mefloquine is absorbed with a half-life of 1 to 4 hours and a time to peak concentration of 7 to 24 hours (median 16.7 hours). Mean peak blood concentrations have ranged between 50 and 110 (median 83) ng/ml/mg/kg. Estimates of total apparent volume of distribution (Vd/f) have ranged from 13.3 to 40.9 (median 19.2) L/kg, systemic clearance (CL/f) from 0.022 to 0.073 L/h/kg (median 0.026 L/h/kg), and terminal elimination half-life from 13.8 to 40.9 days (median 20 days). Systemic clearance appears to be increased in late pregnancy. In uncomplicated falciparum malaria, peak blood concentrations are 2 to 3 times higher than those in healthy subjects ranging from 112 to 209 (median 144) ng/ml/mg/kg because of contraction in the total apparent volume of distribution. Systemic clearance is usually reduced but elimination rates are increased (possibly because of reduced enterohepatic recycling). Mefloquine absorption appears to be reduced in severe falciparum malaria; plasma protein binding exceeds 98% in both healthy subjects and patients. No important drug interactions have been identified as yet, but the potential for serious interactions with quinine has not been adequately investigated. More studies are needed on the disposition of mefloquine in children.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold PJ, Stetten OV. High performance liquid Chromatographic analysis of mefloquine and its metabolites by direct plasma injection with pre-column enrichment and column switching techniques. Journal of Chromatography 353: 193–200, 1986
Bergqvist Y, Churchill FC, Mount DL. Determination of mefloquine by electron capture gas chromatography after phosgene derivatisation in biological samples and in capillary blood collected on filter paper. Journal of Chromatography 428: 281–290, 1988a
Bergqvist Y, Hellgren U, Churchill FC. High performance liquid Chromatographic assay for the simultaneous monitoring of mefloquine and its acid metabolite in biological samples using protein precipitation and ion-pair extraction. Journal of Chromatography 432: 253–263, 1988b
Chanthavanich P, Looareesuwan S, White NJ, Warrell DA, Warrell MJ, et al. Intragastric mefloquine is absorbed rapidly in patients with cerebral malaria. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 34: 1028–1036, 1985
Chongsuphajaisiddhi T, Sabcharoen A, Chantavanich P, Singhasivanon P, Attanath P, et al. A phase-III clinical trial of mefloquine in children with chloroquine-resistant falciparum malaria in Thailand. Bulletin of the World Health Organization 65: 223–226, 1987
Dadgar D, Climax J, Lambe R, Darragh A. Gas Chromatographie determination of mefloquine in human and dog plasma using electron-capture detection. Journal of Chromatography 37: 47–54, 1985
Desjardins RE, Pamplin CL, Von Bredow J, Barry KG, Canfield CJ Kinetics of a new antimalanal mefloquine. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 26: 372–379, 1979
De Souza JM. A phase I clinical trial of mefloquine in Brazilian male subjects. Bulletin of the World Health Organization 61: 809–814, 1983a
De Souza JM. A phase II clinical trial of mefloquine in Brazilian male subjects. Bulletin of the World Health Organization 61: 815–820, 1983b
De Souza JM, Heizmann P, Schwartz DE. Single dose kinetics of mefloquine in Brazilian male subjects. Bulletin of the World Health Organization 65: 353–356, 1987
De Souza JM, Sheth UK, De Oliveira RMG, Roulet H, De Souza SD. An open randomized, phase III clinical trial of mefloquine and of quinine plus sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine in the treatment of symptomatic falciparum malaria in Brazil. Bulletin of the World Health Organization 63: 603–609, 1985
Doberstyn EB, Phintuyothin P, Noeypatimanondh S, Teerakiarkamjorn C. Single dose therapy of falciparum malaria with mefloquine or pyrimethamine-sulfadoxine. Bulletin of the World Health Organization 57: 275–279, 1979
Ekue KMK, Ulrich AM, Rwawogo J, Sheth UK. A double blind comparative clinical trial of mefloquine and chloroquine in symptomatic falciparum malaria. Bulletin of the World Health Organization 61: 713–718, 1983
Fitch CD, Chan RL, Chevli R. Chloroquine resistance in malaria: accessibility of drug receptors to mefloquine. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 15: 258–262, 1979
Franssen G, Rouveix B, Lebras J, Bauchet J, Verdier F, et al. Divided-dose kinetics of mefloquine in man. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 28: 179–184, 1989
Grindel JM, Tilton PF, Shaffer. Quantitation of the antimalarial agent mefloquine in blood, plasma and urine using high pressure liquid chromatography. Journal of Pharmaceutical Science 66: 834–836, 1979
Harinasuta T, Bunnag D, Lasserre R, Leimer R, Vanijanond S. Trials of mefloquine in vivax and of mefloquine plus ‘Fansidar’ in falciparum malaria. Lancet 1: 885–888, 1985
Harinasuta T, Bunnag D, Vanijanond S, Charoenlarp P, Sujntarasamai P, et al. Mefloquine, sulfadoxine and pyrimethamine in the treatment of symptomatic falciparum malaria: a double-blind trial for determining the most effective dose. Bulletin of the World Health Organization 3: 363–367, 1987
Harinasuta T, Bunnag D, Werndorfer WH. A phase II clinical trial of mefloquine in patients with chloroquine-resistant falciparum malaria in Thailand. Bulletin of the World Health Organization 61(2): 299–305, 1983
Heizman P, Geschke R. Determination of the antimalarial mefloquine in human plasma by gas chromatography with electron-capture detection. Journal of Chromatography 311: 411–417, 1984
von Jauch R, Greisser E, Oesterhelt G. Metabolismus von Ro 21–5998 (mefloquine) bei der Ratte. Arzneimittel-Forschung 30: 60–66, 1980
Jiang JB, Li GQ, Guo XB, Kong YC, Arnold K. Antimalarial activity of mefloquine and qinghaosu. Lancet 1: 285–288, 1982
Juma FD, Ogeto JO. Mefloquine disposition in normals and in patients with severe Plasmodium falciparum malaria. European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics 14: 15–18, 1989
Kapetanovic IM, Digiovanni JD, Bartosevich J, Melendez V, von Bredow J, et al. Analysis of the antimalarial mefloquine in blood and plasma using high performance liquid chromatography. Journal of Chromatography 277: 209–215, 1983
Karbwang J, Back DJ, Bunnag D, Breckenridge AM, A comparison of the pharmacokinetics of mefloquine in healthy Thai volunteers and in Thai patients with falciparum malaria. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 35: 677–680, 1988a
Karbwang J, Bunnag D, Breckenridge AM, Back DJ. The pharmacokinetics of mefloquine when given alone or in combination with sulfadoxine and pyrimethamine in Thai male and female subjects. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 32: 173–177, 1987b
Karbwang J, Looareesuwan S, Back DJ, Migasena S, Bunnag D, et al. Effect of oral contraceptive steroids on the clinical course of malaria infection and on the pharmacokinetics of mefloquine in Thai women. Bulletin of the World Health Organization 66: 763–767, 1988b
Karbwang J, Looareesuwan S, Phillips RE, Wattanagoon Y, Molyneux ME, et al. Plasma and whole blood mefloquine concentrations during treatment of chloroquine-resistant falciparum malaria with the combination mefloquine-sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 23: 477–481, 1987a
Karbwang J, Molunto P, Na Bangchang K, Bunnag D. Determination of mefloquine in biological fluids using high performance liquid chromatography. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 20: 55–60, 1989a
Karbwang J, Na Bangchang K, Supapochana A, Bunnag D, Harinasuta T. Pharmacokinetics of prophylactic mefloquine in Thai healthy volunteers. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health, in press, 1989b
Looareesuwan S, White NJ, Warrell DA, Forgo I, Dubach UC, et al. Studies of mefloquine bioavailability and kinetics using a stable isotope technique: a comparison of Thai patients with falciparum malaria and health Caucasian volunteers. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 24: 37–42, 1987
Looareesuwan S, Charoenpan P, Ho M, White NJ, Karbwang J, et al. Fatal Plasmodium falciparum malaria after an inadequate response to quinine treatment. Journal of Infectious Diseases, in press, 1990
Mansor SM, Navaratnam V, Mohamad M, Hussein S, Kumar A. et al. Single dose kinetic study of the triple combination mefloquine-sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine (Fansimef) in healthy male volunteers. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 27: 381–386, 1989
Mimica I, Fry W, Eckert G, Schwartz DE. Multiple dose kinetic study of mefloquine in healthy male volunteers. Chemotherapy 29: 184–187, 1983
Mu JY, Israili ZH, Dayton PG. Studies of the disposition and metabolism of mefloquine HCL (WR 142,149), a quinolinemethanol antimalarial, in the rat. Drug Metabolism and Disposition 3: 198–210, 1975
Na Bangchang, Karbwang J, Back DJ, Bunnag D, Harinasuta T. Clinical pharmacology of mefloquine. IIIrd National Congress of Malaria, Chiangmai, Thailand. Abstract, p. 163, 1989c
Na Bangchang, Karbwang J, Bunnag D, Harinasuta T. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of mefloquine in Thai patients with acute uncomplicated falciparum malaria. IIIrd National Congress of Malaria, Chiangmai, Thailand, Abstract, p. 103, 1989a
Na Bangchang, Karbwang J, Davis T. Looareesuwan S, Pukrittayakamee S, et al. Absorption kinetics of mefloquine in pregnant patients with chloroquine-resistant falciparum malaria. Proceedings of the British Pharmacological Society, p. 108, Manchester, September 13-15, 1989b
Nakagawa T, Higuchi J, Haslam L, Shaffer RD, Mendenhall DW. GLC determination of whole blood antimalarial concentrations. Journal of Pharmaceutical Science 68: 718–721, 1979
Patchen LC, Campbell CC, Williams SB. Neurologic reactions after a therapeutic dose of mefloquine. New England Journal of Medicine 321: 1415–1416, 1989
Riviere JH, Back DJ, Breckenridge AM, Howells RE. The pharmacokinetics of mefloquine in man: lack of effect of mefloquine on antipyrine metabolism. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 20: 469–474, 1985
Rozman RS, Molek NA, Koby R. The absorption, distribution and excretion in mice of the antimalarial mefloquine, erythro-2, 8-bis (trifluoromethyl)-(2-piperidyl)-4-quinolinemethanol hydrochloride. Drug Metabolism and Disposition 6: 654–658, 1978
San George RC, Nagel RL, Fabryl ME. On the mechanism for the red-cell accumulation of mefloquine, an antimalarial drug. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 803: 174–181, 1984
Schwartz DE. Quantitative determination of the antimalarial drug mefloquine and its main metabolite in plasma by direct densitometric measurement on TLC-plates. In Frigero & McCamish (Eds) Recent developments in chromatography and electrophoresis, Vol. 10, pp. 69–74, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1980
Schwartz DE, Eckert G, Ekue JMK. Urinary excretion of mefloquine and some of its metabolites in African volunteers at steady state. Chemotherapy 33: 305–308, 1987
Schwartz DE, Eckert G, Hartmann D, Weber B, Richard-Lenoble D, et al. Single dose kinetics of mefloquine in man. Chemotherapy 28: 70–84, 1982
Schwanz DE, Ranalder UB. Highly sensitive and specific determination of mefloquine in biological fluids using gas chromatography mass spectrometry with selected ion monitoring. Biomedical Mass Spectrometry 8: 589–592, 1981
Schwartz DE, Weber W, Richard-Lenoble D, Gentilini M. Kinetic studies of mefloquine and of one of its metabolites. RO 215104. in the dog and in man. Acta Tropica 37: 238–242, 1980
Silamut K, White NJ, Looareesuwan S, Warrell DA. Binding of quinine to plasma proteins in falciparum malaria. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 34: 681–686, 1985
Tin F, Hlaing N, Lasserre R. Single dose treatment of falciparum malaria with mcfloquine: field studies with different doses in semi-immune adults and children in Burma. Bulletin of the World Health Organization 60: 913–917, 1982
Weidekamm E, Schwartz ED, Dubach UC, Weber B. Single dose investigation of possible interaction between the components of the antimalarial combination Fansimef. Chemotherapy 33: 259–265, 1987
White NJ. Clinical pharmacokinetics of the antimalarial drugs. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 10: 187–215, 1985
White NJ. Combination treatment for P. falciparum prophylaxis. Lancet 1: 680–681, 1987
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karbwang, J., White, N.J. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Mefloquine. Clin Pharmacokinet 19, 264–279 (1990). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199019040-00002
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199019040-00002