Abstract
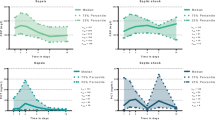
Sepsis-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a serious condition because it is closely linked to the development of multiple organ dysfunctions.We compared molecular fibrinolysis markers for 117 patients with sepsis-induced DIC and 1627 patients with nonseptic DIC. Levels of fibrinogen and fibrin degradation products and D-dimer were significantly lower in sepsis-induced DIC cases than in nonseptic DIC cases. In septic DIC cases, plasma plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1) levels were significantly higher than in nonseptic DIC cases. D-dimer levels were negatively correlated with plasma PAI-1 levels in septic DIC cases. Multiple Organ Dysfunction Scores were significantly higher in septic DIC patients with PAI-1 levels >90 ng/mL than in the group with PAI-1 levels <30 ng/mL. The Kaplan-Meier survival functions until 28 days after DIC diagnosis were significantly lower in the group with PAI-1 levels >90 ng/mL than in the other groups. In a multivariate analysis, plasma PAI-1 levels at DIC diagnosis were an independent risk factor for mortality in sepsis-induced DIC (hazard ratio, 1.012; P = .008). These data suggest that plasma PAI-1 plays an important role in sustaining DIC in septic DIC cases and contributes to multiple organ failure and decreased survival in such patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wheeler AP, Bernard GR. Treating patients with severe sepsis. N Engl J Med. 1999;340:207–214.
Bone RC, Sibbald WJ, Sprung CL. The ACCP-SCCM consensus conference on sepsis and organ failure. Chest. 1992;101:1481–1483.
Thijs LG, de Boer JP, de Groot MC, Hack CE. Coagulation disorders in septic shock. Intensive Care Med. 1993;19(suppl 1):S8-S15.
Levi M, ten Cate H. Disseminated intravascular coagulation. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:586–592.
Rangel-Frausto MS, Pittet D, Costigan M, Hwang T, Davis CS, Wenzel RP. The natural history of the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS): a prospective study. JAMA. 1995;273:117–123.
Baker WF Jr. Clinical aspects of disseminated intravascular coagulation: a clinician’s point of view. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1989;15:1–57.
Taylor FB Jr, Toh CH, Hoots WK, Wada H, Levi M, for the Scientific Subcommittee on Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis (ISYH). Towards definition, clinical and laboratory criteria, and a scoring system for disseminated intravascular coagulation. Thromb Haemost. 2001;86:1327–1330.
Sprengers ED, Kluft C. Plasminogen activator inhibitors. Blood. 1987;69:381–387.
Gando S, Nakanishi Y, Tedo I. Cytokines and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in posttrauma disseminated intravascular coagulation: relationship to multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Crit Care Med. 1995;23:1835–1842.
Gando S, Kameue T, Nanzaki S, Nakanishi Y. Disseminated intravascular coagulation is a frequent complication of systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Thromb Haemost. 1996; 75:224–228.
Mesters RM, Florke N, Ostermann H, Kienast J. Increase of plasminogen activator inhibitor levels predicts outcome of leukocytopenic patients with sepsis. Thromb Haemost. 1996;75:902–907.
Asakura H, Ontachi Y, Mizutani T, et al. An enhanced fibrinolysis prevents the development of multiple organ failure in disseminated intravascular coagulation in spite of much activation of blood coagulation. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:1164–1168.
Kobayashi N, Maekawa T, Takada M, Tanaka H, Gonmori H. Criteria for diagnosis of DIC based on the analysis of clinical and laboratory findings in 345 DIC patients collected by the Research Committee on DIC in Japan. Bibl Haematol. 1983:265–275.
Vincent JL, de Mendonca A, Cantraine F, et al. Use of the SOFA score to assess the incidence of organ dysfunction/failure in intensive care units: results of a multicenter, prospective study. Working Group on “Sepsis-Related Problems” of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Crit Care Med. 1998;26:1793–1800.
American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine Consensus Conference. Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. Crit Care Med. 1992;20:864–874.
Soe G, Kohno I, Inuzuka K, Itoh Y, Matsuda M. A monoclonal antibody that recognizes a neo-antigen exposed in the E domain of fibrin monomer complexed with fibrinogen or its derivatives: its application to the measurement of soluble fibrin in plasma. Blood. 1996;88:2109–2117.
Ono T, Sogabe M, Ogura M, Furusaki F. Automated latex photometric immunoassay for total plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in plasma. Clin Chem. 2003;49:987–989.
Sakata Y, Murakami T, Noro A, Mori K, Matsuda M. The specific activity of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in disseminated intravascular coagulation with acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood. 1991;77:1949–1957.
Slofstra SH, Spek CA, ten Cate H. Disseminated intravascular coagulation. Hematol J. 2003;4:295–302.
Bernard GR, Wheeler AP, Russell JA, et al, for the Ibuprofen in Sepsis Study Group.The effects of ibuprofen on the physiology and survival of patients with sepsis. N Engl J Med. 1997;336:912–918.
Kieft H, Hoepelman AI, Zhou W, Rozenberg-Arska M, Struyvenberg A, Verhoef J. The sepsis syndrome in a Dutch university hospital: clinical observations. Arch Intern Med. 1993;153:2241–2247.
Opal SM, Fisher CJ Jr, Dhainaut JF, et al. Confirmatory interleukin-1 receptor antagonist trial in severe sepsis: a phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. The Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist Sepsis Investigator Group. Crit Care Med. 1997;25:1115–1124.
Jansen PM, Eisele B, de Jong IW, et al. Effect of C1 inhibitor on inflammatory and physiologic response patterns in primates suffering from lethal septic shock. J Immunol. 1998;160:475–484.
Welty-Wolf KE, Carraway MS, Miller DL, et al. Coagulation blockade prevents sepsis-induced respiratory and renal failure in baboons. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164:1988–1996.
Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S, Moss M. The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1546–1554.
Wakabayashi G, Gelfand JA, Jung WK, Connolly RJ, Burke JF, Dinarello CA. Staphylococcus epidermidis induces complement activation, tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1, a shock-like state and tissue injury in rabbits without endotoxemia: comparison to Escherichia coli. J Clin Invest. 1991;87:1925–1935.
Nakasaki T, Wada H, Mori Y, et al. Decreased tissue factor and tissue-plasminogen activator antigen in relapsed acute promyelocytic leukemia. Am J Hematol. 2000;64:145–150.
Wada H, Sakuragawa N, Mori Y, et al. Hemostatic molecular markers before the onset of disseminated intravascular coagulation. Am J Hematol. 1999;60:273–278.
Suffredini AF, Harpel PC, Parrillo JE. Promotion and subsequent inhibition of plasminogen activation after administration of intravenous endotoxin to normal subjects. N Engl J Med. 1989;320:1165–1172.
Levi M, ten Cate H, van der Poll T, van Deventer SJ. Pathogenesis of disseminated intravascular coagulation in sepsis. JAMA. 1993;270:975–979.
Colucci M, Paramo JA, Collen D. Generation in plasma of a fast-acting inhibitor of plasminogen activator in response to endotoxin stimulation. J Clin Invest. 1985;75:818–824.
Paramo JA, Fernandez Diaz FJ, Rocha E. Plasminogen activator inhibitor activity in bacterial infection. Thromb Haemost. 1988;59:451–454.
Pralong G, Calandra T, Glauser MP, et al. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1: a new prognostic marker in septic shock. Thromb Haemost. 1989;61:459–462.
Otto JM, Grenett HE, Fuller GM. The coordinated regulation of fibrinogen gene transcription by hepatocyte-stimulating factor and dexamethasone. J Cell Biol. 1987;105:1067–1072.
Okabayashi K, Wada H, Ohta S, Shiku H, Nobori T, Maruyama K. Hemostatic markers and the sepsis-related organ failure assessment score in patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation in an intensive care unit. Am J Hematol. 2004;76:225–229.
Leithauser B, Matthias FR, Nicolai U, Voss R. Hemostatic abnormalities and the severity of illness in patients at the onset of clinically defined sepsis: possible indication of the degree of endothelial cell activation? Intensive Care Med. 1996;22:631–636.
Dempfle CE. Coagulopathy of sepsis. Thromb Haemost. 2004;91:213–224.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Madoiwa, S., Nunomiya, S., Ono, T. et al. Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor 1 Promotes a Poor Prognosis in Sepsis-Induced Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation. Int J Hematol 84, 398–405 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1532/IJH97.05190
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1532/IJH97.05190