Abstract
Purpose
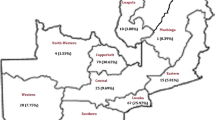
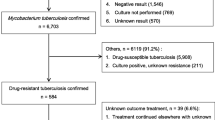
Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) is associated with lengthy treatment, expensive and potentially toxic regimens, and high rates of treatment failure and death. This study describes the outcomes of 351 MDR-TB patients who started treatment between 2004 and 2007 at the provincial MDR-TB referral hospital in Johannesburg, South Africa, and investigates risk factors associated with death.
Methods
The study involved the assessment of factors associated with treatment outcomes using a retrospective review of patient records, drug-susceptibility data and spoligotyping of isolates.
Results
Treatment success (completion/cure) was recorded in 158 (48.8 %) patients, while 65 (20 %) died, 93 (28.7 %) defaulted, 8 (2.5 %) failed treatment, 11(3.1 %) were transferred out to other health facilities and 16 (4.6 %) had no recorded final outcome. The proportion of successful treatment increased significantly over time. Univariable and multivariable analysis (P = 0.05) identified the year of MDR-TB diagnosis and spoligotype-defined families as factors associated with treatment outcome. No associations were found between treatment outcome and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) status, previous TB and additional MDR resistance to streptomycin or ethambutol. Molecular typing of the strains revealed a diverse group of spoligotypes, with Beijing, LAM4 and H3 making up the largest groups.
Conclusions
This is the first published study to investigate treatment outcomes at this facility and to find a link between genotype and treatment outcome, suggesting that genotype determination could potentially serve as a prognostic factor.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Statistics South Africa. Mid-year population estimates 2011. 2011. http://www.statssa.gov.za/publications/P0302/P03022011.pdf.
World Health Organization (WHO). Multidrug and extensively drug-resistant TB (M/XDR-TB): 2010 global report on surveillance and response. WHO/HTM/TB/2010.3. 2010. http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2010/9789241599191_eng.pdf.
World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for the programmatic management of drug-resistant tuberculosis—2011 update. WHO/HTM/TB/2011.6. 2011. http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2011/9789241501583_eng.pdf.
Espinal MA, Kim SJ, Suarez PG, Kam KM, Khomenko AG, Migliori GB, Baéz J, Kochi A, Dye C, Raviglione MC. Standard short-course chemotherapy for drug-resistant tuberculosis: treatment outcomes in 6 countries. JAMA. 2000;283:2537–45.
Bonnet M, Pardini M, Meacci F, Orrù G, Yesilkaya H, Jarosz T, Andrew PW, Barer M, Checchi F, Rinder H, Orefici G, Rüsch-Gerdes S, Fattorini L, Oggioni MR, Melzer J, Niemann S, Varaine F. Treatment of tuberculosis in a region with high drug resistance: outcomes, drug resistance amplification and re-infection. PLoS One. 2011;6:e23081.
Pooran A, Pieterson E, Davids M, Theron G, Dheda K. What is the cost of diagnosis and management of drug resistant tuberculosis in South Africa? PLoS One. 2013;8:e54587.
Bang D, Lillebaek T, Thomsen VØ, Andersen AB. Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: treatment outcome in Denmark, 1992–2007. Scand J Infect Dis. 2010;42:288–93.
Eker B, Ortmann J, Migliori GB, Sotgiu G, Muetterlein R, Centis R, Hoffmann H, Kirsten D, Schaberg T, Ruesch-Gerdes S, Lange C; German TBNET Group. Multidrug- and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis, Germany. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:1700–6.
Orenstein EW, Basu S, Shah NS, Andrews JR, Friedland GH, Moll AP, Gandhi NR, Galvani AP. Treatment outcomes among patients with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2009;9:153–61.
Ahuja SD, Ashkin D, Avendano M, Banerjee R, Bauer M, Bayona JN, Becerra MC, Benedetti A, Burgos M, Centis R, Chan ED, Chiang CY, Cox H, D’Ambrosio L, DeRiemer K, Dung NH, Enarson D, Falzon D, Flanagan K, Flood J, Garcia-Garcia ML, Gandhi N, Granich RM, Hollm-Delgado MG, Holtz TH, Iseman MD, Jarlsberg LG, Keshavjee S, Kim HR, Koh WJ, Lancaster J, Lange C, de Lange WC, Leimane V, Leung CC, Li J, Menzies D, Migliori GB, Mishustin SP, Mitnick CD, Narita M, O’Riordan P, Pai M, Palmero D, Park SK, Pasvol G, Peña J, Pérez-Guzmán C, Quelapio MI, Ponce-de-Leon A, Riekstina V, Robert J, Royce S, Schaaf HS, Seung KJ, Shah L, Shim TS, Shin SS, Shiraishi Y, Sifuentes-Osornio J, Sotgiu G, Strand MJ, Tabarsi P, Tupasi TE, van Altena R, Van der Walt M, Van der Werf TS, Vargas MH, Viiklepp P, Westenhouse J, Yew WW, Yim JJ; Collaborative Group for Meta-Analysis of Individual Patient Data in MDR-TB. Multidrug resistant pulmonary tuberculosis treatment regimens and patient outcomes: an individual patient data meta-analysis of 9,153 patients. PLoS Med. 2012;9:e1001300.
Brust JC, Gandhi NR, Carrara H, Osburn G, Padayatchi N. High treatment failure and default rates for patients with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa, 2000–2003. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2010;14:413–9.
Farley JE, Ram M, Pan W, Waldman S, Cassell GH, Chaisson RE, Weyer K, Lancaster J, Van der Walt M. Outcomes of multi-drug resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) among a cohort of South African patients with high HIV prevalence. PLoS One. 2011;6:e20436.
Satti H, McLaughlin MM, Hedt-Gauthier B, Atwood SS, Omotayo DB, Ntlamelle L, Seung KJ. Outcomes of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis treatment with early initiation of antiretroviral therapy for HIV co-infected patients in Lesotho. PLoS One. 2012;7:e46943.
Gandhi NR, Andrews JR, Brust JC, Montreuil R, Weissman D, Heo M, Moll AP, Friedland GH, Shah NS. Risk factors for mortality among MDR- and XDR-TB patients in a high HIV prevalence setting. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2012;16:90–7.
Shean KP, Willcox PA, Siwendu SN, Laserson KF, Gross L, Kammerer S, Wells CD, Holtz TH. Treatment outcome and follow-up of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis patients, West Coast/Winelands, South Africa, 1992–2002. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2008;12:1182–9.
World Health Organization (WHO) Guidelines for the programmatic management of drug-resistant tuberculosis—emergency update 2008. WHO/HTM/TB/2008.402. 2008. http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2008/9789241547581_eng.pdf.
Van Deun A, Salim MA, Das AP, Bastian I, Portaels F. Results of a standardised regimen for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in Bangladesh. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2004;8:560–7.
Shin SS, Furin JJ, Alcántara F, Bayona J, Sánchez E, Mitnick CD. Long-term follow-up for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12:687–8.
Ferrara G, Richeldi L, Bugiani M, Cirillo D, Besozzi G, Nutini S, Casali L, Fiorentini F, Codecasa LR, Migliori GB. Management of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in Italy. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2005;9:507–13.
Mitnick CD, Franke MF, Rich ML, Alcantara Viru FA, Appleton SC, Atwood SS, Bayona JN, Bonilla CA, Chalco K, Fraser HS, Furin JJ, Guerra D, Hurtado RM, Joseph K, Llaro K, Mestanza L, Mukherjee JS, Muñoz M, Palacios E, Sanchez E, Seung KJ, Shin SS, Sloutsky A, Tolman AW, Becerra MC. Aggressive regimens for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis decrease all-cause mortality. PLoS One. 2013;8:e58664.
Weyer K. DOTs-Plus for standardised management of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in South Africa. Policy guidelines.. Medical Research Council, Pretoria. 2004. http://www.sahealthinfo.org/tb/mdrtbguidelines.pdf.
Rodriguez M, Monedero I, Caminero JA, Encarnación M, Dominguez Y, Acosta I, Muñoz E, Camilo E, Martinez-Selmo S, de los Santos S, del Granado M, Casals M, Cayla J, Marcelino B. Successful management of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis under programme conditions in the Dominican Republic. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2013;17:520–5.
Nkosi D, Janssen S, Padanilam X, Louw R, Menezes CN, Grobusch MP. Factors influencing specialist care referral of multidrug- and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis patients in Gauteng/South Africa: a descriptive questionnaire-based study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2013;13:268.
Padayatchi N, Friedland G. Decentralised management of drug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR- and XDR-TB) in South Africa: an alternative model of care. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2008;12:978–80.
Heller T, Lessells RJ, Wallrauch CG, Bärnighausen T, Cooke GS, Mhlongo L, Master I, Newell ML. Community-based treatment for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in rural KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2010;14:420–6.
Brust JC, Shah NS, Scott M, Chaiyachati K, Lygizos M, van der Merwe TL, Bamber S, Radebe Z, Loveday M, Moll AP, Margot B, Lalloo UG, Friedland GH, Gandhi NR. Integrated, home-based treatment for MDR-TB and HIV in rural South Africa: an alternate model of care. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2012;16:998–1004.
Said HM, Kock MM, Ismail NA, Mphahlele M, Baba K, Omar SV, Osman AG, Hoosen AA, Ehlers MM. Molecular characterization and second-line antituberculosis drug resistance patterns of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from the northern region of South Africa. J Clin Microbiol. 2012;50:2857–62.
Marais BJ, Mlambo CK, Rastogi N, Zozio T, Duse AG, Victor TC, Marais E, Warren RM. Epidemic spread of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in Johannesburg, South Africa. J Clin Microbiol. 2013;51:1818–25.
Chihota VN, Müller B, Mlambo CK, Pillay M, Tait M, Streicher EM, Marais E, van der Spuy GD, Hanekom M, Coetzee G, Trollip A, Hayes C, Bosman ME, Gey van Pittius NC, Victor TC, van Helden PD, Warren RM. Population structure of multi- and extensively drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains in South Africa. J Clin Microbiol. 2012;50:995–1002.
Laserson KF, Thorpe LE, Leimane V, Weyer K, Mitnick CD, Riekstina V, Zarovska E, Rich ML, Fraser HS, Alarcón E, Cegielski JP, Grzemska M, Gupta R, Espinal M. Speaking the same language: treatment outcome definitions for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2005;9:640–5.
Veen J, Raviglione M, Rieder HL, Migliori GB, Graf P, Grzemska M, Zalesky R. Standardized tuberculosis treatment outcome monitoring in Europe. Recommendations of a Working Group of the World Health Organization (WHO) and the European Region of the International Union Against Tuberculosis and Lung Disease (IUATLD) for uniform reporting by cohort analysis of treatment outcome in tuberculosis patients. Eur Respir J. 1998;12:505–10.
Kliiman K, Altraja A. Predictors of poor treatment outcome in multi- and extensively drug-resistant pulmonary TB. Eur Respir J. 2009;33:1085–94.
Holtz TH, Lancaster J, Laserson KF, Wells CD, Thorpe L, Weyer K. Risk factors associated with default from multidrug-resistant tuberculosis treatment, South Africa, 1999–2001. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2006;10:649–55.
Gandhi NR, Moll A, Sturm AW, Pawinski R, Govender T, Lalloo U, Zeller K, Andrews J, Friedland G. Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis as a cause of death in patients co-infected with tuberculosis and HIV in a rural area of South Africa. Lancet. 2006;368:1575–80.
Thiam S, LeFevre AM, Hane F, Ndiaye A, Ba F, Fielding KL, Ndir M, Lienhardt C. Effectiveness of a strategy to improve adherence to tuberculosis treatment in a resource-poor setting: a cluster randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2007;297:380–6.
O’Donnell MR, Padayatchi N, Master I, Osburn G, Horsburgh CR. Improved early results for patients with extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis and HIV in South Africa. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2009;13:855–61.
Dheda K, Lampe FC, Johnson MA, Lipman MC. Outcome of HIV-associated tuberculosis in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. J Infect Dis. 2004;190:1670–6.
Dheda K, Shean K, Zumla A, Badri M, Streicher EM, Page-Shipp L, Willcox P, John MA, Reubenson G, Govindasamy D, Wong M, Padanilam X, Dziwiecki A, van Helden PD, Siwendu S, Jarand J, Menezes CN, Burns A, Victor T, Warren R, Grobusch MP, van der Walt M, Kvasnovsky C. Early treatment outcomes and HIV status of patients with extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis in South Africa: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2010;375:1798–807.
Ebonwu JI, Tint KS, Ihekweazu C. Low treatment initiation rates among multidrug-resistant tuberculosis patients in Gauteng, South Africa, 2011. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2013;17:1043–8.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the staff of the Tuberculosis Referral Laboratory, National Health Laboratory Service, Johannesburg, the Pasteur Institute in Guadeloupe, University of Stellenbosch (Tygerberg) and University of the Witwatersrand (CMID) for their assistance. We thank Dr. A. Dziewiecki, Sizwe Hospital, for the important discussions.
This work was supported by the South African Tuberculosis AIDS Training (SATBAT) programme (National Institutes of Health/Fogarty International Center 1U2RTW007370/3), the Third World Organization for Women in Science (TWOWS), University of the Witwatersrand Health Sciences, European Regional Development Fund, European Commission (ERDF/FEDER, A34-05) and the Regional Council of Guadeloupe (Biodiversity project, CR08/031380), Medical Research Council of South Africa and the DST/NRF Centre of Excellence for Biomedical TB Research. Dr. Zozio was awarded a Ph.D. fellowship by the European Social Funds through the Regional Council of Guadeloupe. James Lewis was funded by the Consortium to Respond Effectively to the AIDS/TB Epidemic (CREATE), United States, who received funding from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marais, E., Mlambo, C.K., Lewis, J.J. et al. Treatment outcomes of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis patients in Gauteng, South Africa. Infection 42, 405–413 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-013-0572-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-013-0572-2