Abstract
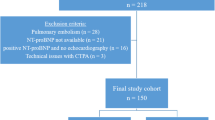
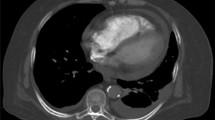
The PROTECT study is designed to assess the prognostic significance of multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) findings in normotensive outpatients with pulmonary embolism (PE). MDCT assesses right ventricular dysfunction (RVD) by measuring the ratio of the right-to-left ventricular short axis diameters. The study uses 30-day all-cause mortality as the primary outcome. The study determined inter- and intraobserver reproducibility of CT findings of RVD. According to the local radiologists’ measurements, 44 % of patients (42/96) showed RVD (defined as a ratio of the RV to the LV short axis greater than 0.9). The intraclass correlation was good (0.773, CI 95 %, 0.678–0.842). For interobserver reproducibility, the weighted kappa measurement was 0.730. Intraobserver reproducibility was very good (0.932, 95 % CI, 0.880–0.962). The PROTECT study is designed to show the prognostic significance of MDCT for PE. Inter- and intraobserver agreement of interpretation of RVD were good.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goldhaber SZ, De Rosa M (1999) Acute pulmonary embolism: clinical outcomes in the international cooperative pulmonary embolism registry. Lancet 353:24–27
Douketis JD, Bates S, Duku EK, Ginsberg JS (1998) Risk of fatal pulmonary embolism in patients with treated venous thromboembolism. J Am Med Assoc 279:458–462
Buller HR, Decousus H, Gallus A, Gent M, Piovella F, Prins MH, Raskob G, van den Berg-Segers AE, Cariou R, et al.; Matisse Investigators. Subcutaneous fondaparinux versus intravenous unfractionated heparin in the initial treatment of pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med 2003; 349: 1695–1702
Jimenez D, Yusen RD, Otero R et al (2007) Prognostic models for selecting patients with acute pulmonary embolism for initial outpatient therapy. Chest 132:24–30
Aujesky D, Perrier A, Roy PM et al (2007) Validation of a clinical prognostic model to identify low-risk patients with pulmonary embolism. J Intern Med 261:597–604
Jaff MR, Archer SL, Cushman M, Goldenberg N, Goldhaber SZ, Jenkins S, Kline JA, Michaels AD, Thistlethwaite P, Vedantham S, White RJ, Zierler BK (2011) On behalf of the American Heart, Association Council on Cardiopulmonary CC, Perioperative and Resuscitation, Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease, and Council on Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology. Management of Massive and Submassive Pulmonary Embolism, Iliofemoral Deep Vein Thrombosis, and Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 123:1788–1830
Jimenez D, Yusen RD (2010) Risk stratification of normotensive patients with acute symptomatic pulmonary embolism. Br J Haematol 151:415–424
Jiménez D, Moores L, Gómez V, Lobo JL, Uresandi F, Otero R, Monreal M, Muriel A, Yusen RD; RIETE Investigators. Simplification of the pulmonary embolism severity index for prognostication in patients with acute symptomatic pulmonary embolism. Arch Intern Med 2010; 170:1383–1389
Goldhaber SZ (2002) Echocardiography in the management of pulmonary embolism. Ann Intern Med 136:691–700
Lang RM, Bierig M, Devereux RB et al (2005) Recommendations for chamber quantification: a report from the American Society of Echocardiography’s Guidelines and Standards Committee and the Chamber Quantification Writing Group, developed in conjunction with the European Association of Echocardiography, a branch of the European Society of Cardiology. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 18:1440–1463
Dell’Italia LJ (1991) The right ventricle: anatomy, physiology, and clinical importance. Curr Probl Cardiol 16:653–720
Torbicki A, Perrier A, Konstantinides S, Agnelli G, Galiè N, Pruszczyk P, Bengel F, Brady AJ, Ferreira D, Janssens U, Klepetko W, Mayer E, Remy-Jardin M, Bassand JP, Vahanian A, Camm J, De Caterina R, Dean V, Dickstein K, Filippatos G, Funck-Brentano C, Hellemans I, Kristensen SD, McGregor K, Sechtem U, Silber S, Tendera M, Widimsky P, Zamorano JL, Zamorano JL, Andreotti F, Ascherman M, Athanassopoulos G, De Sutter J, Fitzmaurice D, Forster T, Heras M, Jondeau G, Kjeldsen K, Knuuti J, Lang I, Lenzen M, Lopez-Sendon J, Nihoyannopoulos P, Perez Isla L, Schwehr U, Torraca L, Vachiery JL (2008) Task force for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J 29:2276–2315
Stein PD, Fowler SE, Goodman LR, Gottschalk A, Hales CA, Hull RD, Leeper KV Jr, Popovich J Jr, Quinn DA, Sos TA, Sostman HD, Tapson VF, Wakefield TW, Weg JG, Woodard PK; PIOPED II Investigators. Multidetector computed tomography for acute pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med 2006; 354: 2317–2327
Perrier A, Roy PM, Sanchez O, Le Gal G, Meyer G, Gourdier AL, Furber A, Revel MP, Howarth N, Davido A, Bounameaux H (2005) Multidetector-row computed tomography in suspected pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med 352:1760–1768
van Belle A, Buller HR, Huisman MV, Huisman PM, Kaasjager K, Kamphuisen PW, Kramer MH, Kruip MJ, Kwakkel-van Erp JM, Leebeek FW, Nijkeuter M, Prins MH, Sohne M, Tick LW; Christopher Study Investigators. Effectiveness of managing suspected pulmonary embolism using an algorithm combining clinical probability, D-dimer testing, and computed tomography. JAMA 2006; 295: 172–179
Schoepf UJ, Kucher N, Kipfmueller F, Quiroz R, Costello P, Goldhaber SZ (2004) Right ventricular enlargement on chest computed tomography: a predictor of early death in acute pulmonary embolism. Circulation 110:3276–3280
Araoz PA, Gotway MB, Harrington JR, Harmsen WS, Mandrekar JN (2007) Pulmonary embolism: prognostic CT findings. Radiology 242:889–897
van der Meer RW, Pattynama PM, van Strijen MJ, van den Berg-Huijsmans AA, Hartmann IJ, Putter H, de Roos A, Huisman MV (2005) Right ventricular dysfunction and pulmonary obstruction index at helical CT: prediction of clinical outcome during 3-month follow-up in patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Radiology 235:798–803
Quiroz R, Kucher N, Schoepf J, Quiroz R, Costello P, Goldhaber SZ (2004) Right ventricular enlargement on chest computed tomography. Prognostic role in acute pulmonary embolism. Circulation 109:2401–2404
Remy-Jardin M, Remy J, Wattinne L, Giraud F (1992) Central pulmonary thromboembolism: diagnosis with spiral volumetric CT with the single-breath-hold-technique-comparison with pulmonary angiography. Radiology 185:381–387
Stein PD, Beemath A, Matta F, Goodman LR, Weg JG, Hales CA, Hull RD, Leeper KV, Sostman D, Woodward PK (2008) Enlarged right ventricle without shock in acute pulmonary embolism: prognosis. Am J Med 121:34–42
Grifoni S, Olivotto I, Cecchini P, Pieralli F, Camaiti A, Santoro G, Conti A, Agnelli G, Berni G (2000) Short term clinical outcome of patients with pulmonary embolism, normal blood pressure and echocardiographic right ventricular dysfunction. Circulation 101:2817–2822
Sanchez O, Trinquart L, Caille V, Couturaud F, Pacouret G, Meneveau N, Verschuren F, Roy PM, Parent F, Righini M, Perrier A, Lorut C, Tardy B, Benoit MO, Chatellier G, Meyer G (2010) Prognostic factors for pulmonary embolism: the PREP study, a prospective multicenter cohort study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 181:168–173
Jiménez D, Díaz G, Molina J, Martí D, Del Rey J, García-Rull S, Escobar C, Vidal R, Sueiro A, Yusen RD (2008) Troponin I and risk stratification of patients with acute nonmassive pulmonary embolism. Eur Respir J 31:847–853
Pieralli F, Olivotto I, Vanni S, Conti A, Camaiti A, Targioni G, Grifoni S, Berni G (2006) Usefulness of bedside testing for brain natriuretic peptide to identify right ventricular dysfunction and outcome in normotensive patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Am J Cardiol 97:1386–1390
Aujesky D, Obrosky DS, Stone RA, Auble TE, Perrier A, Cornuz J, Roy PM, Fine MJ (2005) Derivation and validation of a prognostic model for pulmonary embolism. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 172:1041–1046
Bauersachs R, Berkowitz SD, Brenner B, Buller HR, Decousus H, Gallus AS, Lensing AW, Misselwitz F, Prins MH, Raskob GE, Segers A, Verhamme P, Wells P, Agnelli G, Bounameaux H, Cohen A, Davidson BL, Piovella F, Schellong S (2011) Oral rivaroxaban for symptomatic venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med 363:2499–2510
Von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, Pocock SJ, Gøtzsche PC (2007) STROBE Initiative. The strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. Ann Intern Med 147:573–577
Harrel FE Jr, Lee KL, Mark DB (1996) Multivariable prognostic models: issues in developing models, evaluating assumptions and adequacy, and measuring and reducing errors. Stat Med 15:361–387
Pencina MJ, D’Agostino RB (2004) Overall C as a measure of discrimination in survival analysis: model specific population value and confidence interval estimation. Stat Med 23:2109–2123
Hosmer DW Jr, Lemeshow S (1989) Applied logistic regression. Wiley, New York
Little RJ, Rubin DB (1987) Statistical analysis with missing data. Wiley, New York
Rubin DB, Schenker N (1991) Multiple imputation in health-care databases: an overview and some applications. Stat Med 10:585–598
Bland JM, Altman DG (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1:307–310
Altman DG (1991) Practical statistics for medical research. Chapman and Hall, London, p 404
Jiménez D, Aujesky D, Moores L, Gómez V, Martí D, Briongos S, Monreal M, Barrios V, Konstantinides S, Yusen RD (2011) Combinations of prognostic tools for identification of high-risk normotensive patients with acute symptomatic pulmonary embolism. Thorax 66:75–81
Kang DK, Thilo C, Schoepf J, Barraza JM, Nance JW, Bastarrika G, Abro JA, Ravenel JG, Costello P, Goldhaber SZ (2011) CT signs of right ventricular dysfunction. Prognostic role in acute pulmonary embolism. J Am Coll Cardiol Img 4:841–849
Becattini C, Agnelli G, Vedovati MC (2011) Multidetector computed tomography for acute pulmonary embolism: diagnosis and risk stratification in a single test. Eur Heart J 32:1657–1663
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was conducted on behalf of the PROTECT investigators. The members of the PROTECT investigation are given in the Appendix.
Appendices
Appendix
Coordinator of the PROTECT Study: David Jiménez.
PROTECT Steering Committee Members: David Jiménez, José Luis Lobo, Manuel Monreal, Remedios Otero, Roger D. Yusen.
PROTECT Study Coordinating Center: S & H Medical Science Service.
Data and Safety Monitoring Board: Francisco Conget, Dolores Nauffal, Mikel Oribe, Fernando Uresandi.
Radiological Panel: Ignacio Gallego, Luis Gorospe, Agustina Vicente.
Blood Sample Processing: José Manuel del Rey.
Statiscian: Víctor Abraira, Javier Zamora, Alfonso Muriel.
Investigators of the PROTECT study
Consolación Rodríguez, Jorge Vivancos, Jesús Marín (Bormujos), Mikel Oribe, Aitor Ballaz, Jose María Abaitúa, Sonia Velasco (Galdakao), Manuel Barrón, María Lladó, Carmen Rodrigo, Luis Javier Alonso (Logroño), Ramón Rabuñal, Olalla Castro, Concepción Iglesias, Ana Testa (Lugo), David Jiménez, Vicente Gómez, Luis Gorospe, Sem Briongos, José Manuel del Rey (Madrid), Celso Álvarez, Nuria Rodríguez, Amador Prieto, María Martín (Oviedo), Carmen Navarro, Mónica López, Eva Castañer, Eva Guillaumet (Sabadell), Remedios Otero, Teresa Elías, Pilar Serrano, Francisco López (Sevilla), Reina Valle, María Victoria Piret, Pilar Lucio, José María Cuesta (Sierrallana), Dolores Nauffal, Marta Ballester, José Pamies, Ana Osa (Valencia), José Luis Lobo, Vanesa Zorrilla, Delfina Pozo, Ángel Alonso (Vitoria), Francisco Conget, Miguel Ángel Santolaria, Mariano González, José Luis de Benito (Zaragoza).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiménez, D., Lobo, J.L., Monreal, M. et al. Prognostic significance of multidetector computed tomography in normotensive patients with pulmonary embolism: rationale, methodology and reproducibility for the PROTECT study. J Thromb Thrombolysis 34, 187–192 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-012-0709-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-012-0709-7