Abstract
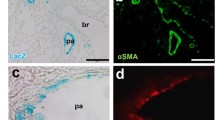
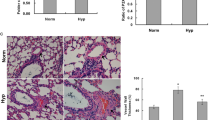
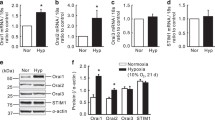
Phenotype modulation of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMCs) plays an important role during hypoxia-induced vascular remodeling and pulmonary hypertension (PAH). We had previously shown that calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) is expressed in rat PASMCs. However, little is known about the role of CaSR in phenotypic modulation of PASMCs in hypoxia-induced PAH as well as the underlying mechanisms. In this study, we investigated whether CaSR induces the proliferation of PASMCs in small pulmonary arteries from both rats and human with PAH. PAH was induced by exposing rats to hypoxia for 7–21 days. The mean pulmonary arterial pressure (mPAP), right ventricular hypertrophy index (RVI), the percentage of medial wall thickness to the external diameter (WT %), and cross-sectional total vessel wall area to the total area (WA %) of small pulmonary arteries were determined by hematoxylin and eosin (HE), masson trichrome and Weigert’s staining. The protein expressions of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9, the tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase (TIMP)-3, CaSR, proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (p-ERK), and smooth muscle cell (SMC) phenotype marker proteins in rat small pulmonary arteries, including calponin, SMα-actin (SMAα), and osteopontin (OPN), were analyzed by immunohistochemistry and Western blotting, respectively. In addition, immunohistochemistry was applied to paraffin-embedded human tissues from lungs of normal human and PAH patients with chronic heart failure (PAH/CHF). Compared with the control group, mPAP, RVI, WT % and WA % in PAH rats were gradually increased with the prolonged hypoxia. At the same time, the expressions of CaSR, MMP-2, MMP-9, TIMP-3, PCNA, OPN, and p-ERK were markedly increased, while the expressions of SMAα and calponin were significantly reduced in lung tissues or small pulmonary arteries of PAH rats. Neomycin (an agonist of CaSR) enhanced but NPS2390 (an antagonist of CaSR) weakened these hypoxic effects. We further found that the expression change of CaSR, PCNA, and SMC phenotypic marker proteins in PAH/CHF lungs was similar to those in PAH rats. Our data suggest that CaSR is involved in the pulmonary vascular remodeling and PAH by promoting phenotypic modulation of small pulmonary arteries.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schermuly RT, Ghofrani HA, Wilkins MR, Grimminger F (2011) Mechanisms of disease: pulmonary arterial hypertension. Nat Rev Cardiol 8:443–455. doi:10.1038/nrcardio.2011.87
Guo Q, Huang JA, Yamamura A, Yamamura H, Zimnicka AM, Fernandez R, Yuan JX (2014) Inhibition of the Ca(2+)-sensing receptor rescues pulmonary hypertension in rats and mice. Hypertens Res 37:116–124. doi:10.1038/hr.2013.129
Archer SL, Weir EK, Wilkins MR (2010) Basic science of pulmonary arterial hypertension for clinicians: new concepts and experimental therapies. Circulation 121:2045–2066. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.847707
Jie W, Guo J, Shen Z, Wang X, Zheng S, Wang G, Ao Q (2010) Contribution of myocardin in the hypoxia-induced phenotypic switching of rat pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. Exp Mol Pathol 89:301–306. doi:10.1016/j.yexmp.2010.06.010
Frid MG, Moiseeva EP, Stenmark KR (1994) Multiple phenotypically distinct smooth muscle cell populations exist in the adult and developing bovine pulmonary arterial media in vivo. Circ Res 75:669–681
House SJ, Ginnan RG, Armstrong SE, Singer HA (2007) Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II-delta isoform regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 292:C2276–C2287. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00606.2006
Song MY, Makino A, Yuan JX (2011) STIM2 Contributes to enhanced store-operated ca entry in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells from patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pulm Circ 1:84–94. doi:10.4103/2045-8932.78106
Fuchs B, Dietrich A, Gudermann T, Kalwa H, Grimminger F, Weissmann N (2010) The role of classical transient receptor potential channels in the regulation of hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction. Adv Exp Med Biol 661:187–200. doi:10.1007/978-1-60761-500-2_12
Lin MJ, Leung GP, Zhang WM, Yang XR, Yip KP, Tse CM, Sham JS (2004) Chronic hypoxia-induced upregulation of store-operated and receptor-operated Ca2+ channels in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells: a novel mechanism of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Circ Res 95:496–505. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000138952.16382.ad
Magno AL, Ward BK, Ratajczak T (2010) The calcium-sensing receptor: a molecular perspective. Endocr Rev 32:3–30
Hofer AM, Brown EM (2003) Extracellular calcium sensing and signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:530–538
Brown EM, MacLeod RJ (2001) Extracellular calcium sensing and extracellular calcium signaling. Physiol Rev 81:239–297
Wang R, Xu C, Zhao W, Zhang J, Cao K, Yang B, Wu L (2003) Calcium and polyamine regulated calcium-sensing receptors in cardiac tissues. Eur J Biochem 270:2680–2688
Li GW, Wang QS, Hao JH, Xing WJ, Guo J, Li HZ, Bai SZ, Li HX, Zhang WH, Yang BF, Yang GD, Wu LY, Wang R, Xu CQ (2011) The functional expression of extracellular calcium-sensing receptor in rat pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. J Biomed Sci 18:16. doi:10.1186/1423-0127-18-16
Chow JY, Estrema C, Orneles T, Dong X, Barrett KE, Dong H (2011) Calcium-sensing receptor modulates extracellular Ca2+ entry via TRPC-encoded receptor-operated channels in human aortic smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 301:C461
Weston AH, Absi M, Ward DT, Ohanian J, Dodd RH, Dauban P, Petrel C, Ruat M, Edwards G (2005) Evidence in favor of a calcium-sensing receptor in arterial endothelial cells studies with calindol and calhex 231. Circ Res 97:391–398
Zhang J, Zhou J, Cai L, Lu Y, Wang T, Zhu L, Hu Q (2012) Extracellular calcium-sensing receptor is critical in hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction. Antioxid Redox Signal 17:471–484. doi:10.1089/ars.2011.4168
Yamamura A, Guo Q, Yamamura H, Zimnicka AM, Pohl NM, Smith KA, Fernandez RA, Zeifman A, Makino A, Dong H, Yuan JX (2012) Enhanced Ca(2+)-sensing receptor function in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circ Res 111:469–481. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.266361
Wang J, Weigand L, Wang W, Sylvester JT, Shimoda LA (2005) Chronic hypoxia inhibits Kv channel gene expression in rat distal pulmonary artery. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 288:L1049–L1058. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00379.2004
Lee SJ, Smith A, Guo L, Alastalo TP, Li M, Sawada H, Liu X, Chen ZH, Ifedigbo E, Jin Y, Feghali-Bostwick C, Ryter SW, Kim HP, Rabinovitch M, Choi AM (2011) Autophagic protein LC3B confers resistance against hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 183:649–658. doi:10.1164/rccm.201005-0746OC
Liu Y, Tian XY, Mao G, Fang X, Fung ML, Shyy JY, Huang Y, Wang N (2012) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma ameliorates pulmonary arterial hypertension by inhibiting 5-hydroxytryptamine 2B receptor. Hypertension 60:1471–1478. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.112.198887
Sun Y, Tian Y, Prabha M, Liu D, Chen S, Zhang R, Liu X, Tang C, Tang X, Jin H, Du J (2010) Effects of sulfur dioxide on hypoxic pulmonary vascular structural remodeling. Lab Invest 90:68–82. doi:10.1038/labinvest.2009.102
Nijenhuis T, Vallon V, van der Kemp AW, Loffing J, Hoenderop JG, Bindels RJ (2005) Enhanced passive Ca2+ reabsorption and reduced Mg2+ channel abundance explains thiazide-induced hypocalciuria and hypomagnesemia. J Clin Invest 115:1651–1658. doi:10.1172/JCI24134
Huang X, Fan R, Lu Y, Yu C, Xu X, Zhang X, Liu P, Yan S, Chen C, Wang L (2014) Regulatory effect of AMP-activated protein kinase on pulmonary hypertension induced by chronic hypoxia in rats: in vivo and in vitro studies. Mol Biol Rep. doi:10.1007/s11033-014-3272-9
Newby AC (2006) Matrix metalloproteinases regulate migration, proliferation, and death of vascular smooth muscle cells by degrading matrix and non-matrix substrates. Cardiovasc Res 69:614–624. doi:10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.08.002
Daniel JM, Sedding DG (2011) Circulating smooth muscle progenitor cells in arterial remodeling. J Mol Cell Cardiol 50:273–279. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2010.10.030
Lepetit H, Eddahibi S, Fadel E, Frisdal E, Munaut C, Noel A, Humbert M, Adnot S, D’Ortho MP, Lafuma C (2005) Smooth muscle cell matrix metalloproteinases in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur Respir J 25:834–842. doi:10.1183/09031936.05.00072504
Fernandez RA, Sundivakkam P, Smith KA, Zeifman AS, Drennan AR, Yuan JX (2012) Pathogenic role of store-operated and receptor-operated ca(2+) channels in pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Signal Transduct 2012:951497. doi:10.1155/2012/951497
Kuhr FK, Smith KA, Song MY, Levitan I, Yuan JX (2012) New mechanisms of pulmonary arterial hypertension: role of Ca(2+) signaling. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 302:H1546–H1562. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00944.2011
Riccardi D (2012) Parathyroid hormone-independent role for the calcium-sensing receptor in the control of urinary calcium excretion. J Am Soc Nephrol 23:1766–1768. doi:10.1681/ASN.2012090955
Guo Q, Huang JA, Yamamura A, Yamamura H, Zimnicka AM, Fernandez R, Yuan JX (2013) Inhibition of the Ca-sensing receptor rescues pulmonary hypertension in rats and mice. Hypertens Res. doi:10.1038/hr.2013.129
Li GW, Xing WJ, Bai SZ, Hao JH, Guo J, Li HZ, Li HX, Zhang WH, Yang BF, Wu LY, Wang R, Yang GD, Xu CQ (2011) The calcium-sensing receptor mediates hypoxia-induced proliferation of rat pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells through MEK1/ERK1,2 and PI3K pathways. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 108:185–193. doi:10.1111/j.1742-7843.2010.00639.x
Aoshima D, Murata T, Hori M, Ozaki H (2009) Time-dependent phenotypic and contractile changes of pulmonary artery in chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. J Pharmacol Sci 110:182–190
Wang L, Zheng J, Du Y, Huang Y, Li J, Liu B, Liu CJ, Zhu Y, Gao Y, Xu Q, Kong W, Wang X (2010) Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein maintains the contractile phenotype of vascular smooth muscle cells by interacting with alpha(7)beta(1) integrin. Circ Res 106:514–525. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.202762
Yi B, Cui J, Ning JN, Wang GS, Qian GS, Lu KZ (2012) Over-expression of PKGIα inhibits hypoxia-induced proliferation, Akt activation, and phenotype modulation of human PASMCs: the role of phenotype modulation of PASMCs in pulmonary vascular remodeling. Gene 492:354–360. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2011.11.010
Zhao Y, Lv M, Lin H, Cui Y, Wei X, Qin Y, Kohama K, Gao Y (2013) Rho-associated protein kinase isoforms stimulate proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells through ERK and induction of cyclin D1 and PCNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 432:488–493. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.02.009
Reinke C, Bevans-Fonti S, Grigoryev DN, Drager LF, Myers AC, Wise RA, Schwartz AR, Mitzner W, Polotsky VY (2011) Chronic intermittent hypoxia induces lung growth in adult mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 300:L266–L273. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00239.2010
Rzucidlo EM (2009) Signaling pathways regulating vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation. Vascular 17(Suppl 1):S15–S20
Li L, Wang L, Li TT, Li X, Huang XQ, Chen XW, Li ZL, Lv XM, Liu FY, Luo ZW, Liu M, Hu XH, Hu WF, Huang ZX, Yi M, Liu SJ, Liu YZ, Li DW (2013) ERK signaling pathway regulates embryonic survival and eye development in goldfish, Carassius auratus. Curr Mol Med 13:959–967
Avlani VA, Ma W, Mun HC, Leach K, Delbridge L, Christopoulos A, Conigrave AD (2013) Calcium-sensing receptor-dependent activation of CREB phosphorylation in HEK293 cells and human parathyroid cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 304:E1097–E1104. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00054.2013
Lu FH, Fu SB, Leng X, Zhang X, Dong S, Zhao YJ, Ren H, Li H, Zhong X, Xu CQ, Zhang WH (2013) Role of the calcium-sensing receptor in cardiomyocyte apoptosis via the sarcoplasmic reticulum and mitochondrial death pathway in cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. Cell Physiol Biochem 31:728–743. doi:10.1159/000350091
Molostvov G, Fletcher S, Bland R, Zehnder D (2008) Extracellular calcium-sensing receptor mediated signalling is involved in human vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and apoptosis. Cell Physiol Biochem 22:413–422. doi:10.1159/000185484
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81070123, 81270311, 81100191, 81270273, 81200160), the Postdoctoral Research Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (LBH-Z12197), and the Foundation of Heilongjiang Educational Committee (12511618).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, X., Li, HX., Shao, HJ. et al. Involvement of calcium-sensing receptors in hypoxia-induced vascular remodeling and pulmonary hypertension by promoting phenotypic modulation of small pulmonary arteries. Mol Cell Biochem 396, 87–98 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2145-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2145-9