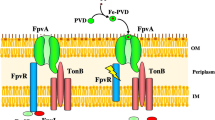
Abstract
The Pseudomonas genus belongs to the γ division of Proteobacteria and many species produce the characteristic yellow–green siderophore pyoverdine, and often a second siderophore, of lower affinity for iron. These bacteria are known for their ability to colonize different ecological niches and for their versatile metabolism. It is therefore not surprising that they are endowed with the capacity to take up exogenous xenosiderophores via different TonB-dependent receptors. Uptake of iron is controlled by the central regulator Fur, and via extracytoplasmic sigma factors or other types of regulators (two-component systems, AraC regulators). In this review the Fur regulon (experimentally proven and/or predicted) of P. aeruginosa will be presented. An interesting feature revealed by this analysis of Fur-regulated genes is the overlap between the iron and the sulfur regulons as well with the quorum sensing system.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews SC, Robinson AK, Rodríguez-Quiñones F (2003) Bacterial iron homeostasis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27:215–237. doi:10.1016/S0168-6445(03)00055-X
Braun V, Mahren S, Sauter A (2006) Gene regulation by transmembrane signaling. Biometals 19:103–113. doi:10.1007/s10534-005-8253-y
Butterton JR, Calderwood SB (1994) Identification, cloning, and sequencing of a gene required for ferric vibriobactin utilization by Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol 176:5631–5638
Dean CR, Poole K (1993) Expression of the ferric enterobactin receptor (PfeA) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: involvement of a two-component regulatory system. Mol Microbiol 8:1095–1103. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01654.x
Dean CR, Neshat S, Poole K (1996) PfeR, an enterobactin responsive activator of ferric enterobactin receptor gene expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 178:5361–5369
Diggle SP, Winzer K, Lazdunski A, Williams P, Cámara M (2002) Advancing the quorum in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: MvaT and the regulation of N-acylhomoserine lactone production and virulence gene expression. J Bacteriol 184:2576–2586. doi:10.1128/JB.184.10.2576-2586.2002
Diggle SP, Cornelis P, Williams P, Cámara M (2006) 4-quinolone signalling in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: old molecules, new perspectives. Int J Med Microbiol 296:83–91. doi:10.1016/j.ijmm.2006.01.038
Escolar L, Pérez-Martín J, de Lorenzo V (1999) Opening the iron box: transcriptional metalloregulation by the Fur protein. J Bacteriol 181:6223–6229
Ghysels B, Dieu BT, Beatson SA, Pirnay JP, Ochsner UA, Vasil ML, Cornelis P (2004) FpvB, an alternative type I ferripyoverdine receptor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiology 150:1671–1680. doi:10.1099/mic.0.27035-0
Ghysels B, Ochsner U, Mollman U, Heinisch L, Vasil M, Cornelis P, Matthijs S (2005) The Pseudomonas aeruginosa pirA gene encodes a second receptor for ferrienterobactin and synthetic catecholate analogues. FEMS Microbiol Lett 246:167–174. doi:10.1016/j.femsle.2005.04.010
Huang B, Ru K, Yuan Z, Whitchurch CB, Mattick JS (2004) tonB3 is required for normal twitching motility and extracellular assembly of type IV pili. J Bacteriol 186:4387–4389. doi:10.1128/JB.186.13.4387-4389.2004
Llamas MA, Sparrius M, Kloet R, Jiménez CR, Vandenbroucke-Grauls C, Bitter W (2006) The heterologous siderophores ferrioxamine B and ferrichrome activate signaling pathways in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 188:1882–1891. doi:10.1128/JB.188.5.1882-1891.2006
Llamas MA, Mooij MJ, Sparrius M, Vandenbroucke-Grauls CMJE, Ratledge C, Bitter W (2008) Characterization of five novel Pseudomonas aeruginosa cell-surface signalling systems. Mol Microbiol 67:458–472
Michel L, Gonzalez N, Jagdeep S, Nguyen-Ngoc T, Reimmann C (2005) PchR-box recognition by the AraC-type regulator PchR of Pseudomonas aeruginosa requires the siderophore pyochelin as an effector. Mol Microbiol 58:495–509. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04837.x
Ochsner UA, Wilderman PJ, Vasil AI, Vasil ML (2002) GeneChip expression analysis of the iron starvation response in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: identification of novel pyoverdine biosynthesis genes. Mol Microbiol 45:1277–1287. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03084.x
Ó Cuív P, Clarke P, O’Connel M (2006) Identification and characterization of an iron-regulated gene, chtA, required for the utilization of the xenosiderophores aerobactin, rhizobactin 1021 and schizokinen by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiology 152:945–954. doi:10.1099/mic.0.28552-0
Oglesby AG, Farrow JM 3rd, Lee JH, Tomaras AP, Greenberg EP, Pesci EC, Vasil ML (2008) The influence of iron on Pseudomonas aeruginosa physiology: a regulatory link between iron and quorum sensing. J Biol Chem 283:15558–15567. doi:10.1074/jbc.M707840200
Palma M, Worgall S, Quadri LE (2003) Transcriptome analysis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa response to iron. Arch Microbiol 180:374–379. doi:10.1007/s00203-003-0602-z
Poole K, Zhao Q, Neshat S, Heinrichs DE, Dean CR (1996) The Pseudomonas aeruginosa tonB gene encodes a novel TonB protein. Microbiology 142:1449–1458
Potvin E, Sanschagrin F, Levesque RC (2008) Sigma factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32:38–55
Ravel J, Cornelis P (2003) Genomics of pyoverdine-mediated iron uptake in pseudomonads. Trends Microbiol 11:195–200
Shea CM, McIntosh MA (1991) Nucleotide sequence and genetic organization of the ferric enterobactin transport system: homology to other periplasmic binding protein-dependent systems in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 5:1415–1428. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00788.x
Tralau T, Vuilleumier S, Thibault C, Campbell BJ, Hart CA, Kertesz MA (2007) Transcriptomic analysis of the sulfate starvation response of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 189:6743–6750. doi:10.1128/JB.00889-07
Vallet I, Diggle SP, Stacey RE, Cámara M, Ventre I, Lory S, Lazdunski A, Williams P, Filloux A (2004) Biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: fimbrial cup gene clusters are controlled by the transcriptional regulator MvaT. J Bacteriol 186:2880–2890. doi:10.1128/JB.186.9.2880-2890.2004
van der Ploeg JR, Weiss MA, Saller E, Nashimoto H, Saito N, Kertesz MA, Leisinger T (1996) Identification of sulfate starvation-regulated genes in Escherichia coli: a gene cluster involved in the utilization of taurine as a sulfur source. J Bacteriol 178:5438–5446
van Oeffelen L, Cornelis P, Van Delm W, De Ridder F, De Moor B, Moreau Y (2008) Detecting cis-regulatory binding sites for cooperatively binding proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 36:e46. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn140
Vasil ML (2006) How we learnt about iron acquisition in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a series of very fortunate events. Biometals 20:587–601. doi:10.1007/s10534-006-9067-2
Vasil ML, Ochsner UA (1999) The response of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to iron: genetics, biochemistry and virulence. Mol Microbiol 34:399–413. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01586.x
Visca P, Imperi F, Lamont IL (2007) Pyoverdine siderophores: from biogenesis to biosignificance. Trends Microbiol 15:22–30. doi:10.1016/j.tim.2006.11.004
Wilderman PJ, Sowa NA, Fitzgerald DJ, Fitzgerald PC, Gottesman S, Ochsner UA, Vasil ML (2004) Identification of tandem duplicate regulatory small RNAs in Pseudomonas aeruginosa involved in iron homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:9792–9797. doi:10.1073/pnas.0403423101
Willemsen PTJ, Vulto I, Boxem M, De Graaff J (1997) Characterization of a periplasmic protein involved in iron utilization of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. J Bacteriol 179:4949–4952
Zhao Q, Poole K (2000) A second tonB gene in Pseudomonas aeruginosa is linked to the exbB and exbD genes. FEMS Microbiol Lett 184:127–132. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2000.tb09002.x
Zhao Q, Poole K (2002) Mutational analysis of the tonB1 energy coupler of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 184:1503–1513. doi:10.1128/JB.184.6.1503-1513.2002
Zheng P, Sun J, Geffers R, Zeng A-P (2007) Functional characterization of the gene PA2384 in large-scale gene regulation in response to iron starvation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biotechnol 132:342–352. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2007.08.013
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cornelis, P., Matthijs, S. & Van Oeffelen, L. Iron uptake regulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa . Biometals 22, 15–22 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-008-9193-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-008-9193-0