Abstract
Background: Immunocompromised patients are prone to develop invasive pulmonary aspergillosis (IPA). Relapse and high mortality rates are seen in those patients who receive subsequent immunotoxic therapy. Standard antifungal regimens often fail to completely eradicate IPA, which then warrants an aggressive surgical approach.
Methods: We performed a retrospective chart review of 13 immunocompromised patients who were considered to have IPA and who underwent surgery between 1988 and 1998.
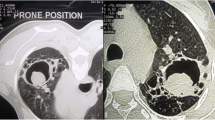
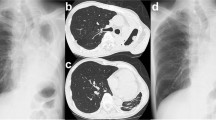
Results: Twelve patients had a hematological malignancy and one patient had breast cancer. The diagnosis of IPA was based on a chest computed tomographic scan in all patients. A preoperative diagnosis of aspergillosis was made in three patients, and mucormycosis in one patient, by bronchoalveolar lavage. Before surgery, seven patients received chemotherapy, one patient underwent bone marrow transplantation, and five patients received a combination of chemotherapy and bone marrow transplantation. Symptoms included cough (54%), fever (54%), hemoptysis (30%), and shortness of breath (8%). Three patients (23%) were asymptomatic. The mean preoperative absolute neutrophil count was 4881 cells/ml. Seventeen thoracic operations were performed, i.e., 12 wedge resections, 4 lobectomies, and 1 pneumonectomy. One patient also underwent nephrectomy for invasive aspergillosis and one patient underwent craniotomy to resect an aspergillus brain mass. Surgical pathology revealed IPA in 13 (76%), invasive mucormycosis in 2 (15%), aspergilloma in 1, and diffuse alveolar hemorrhage in 1. Postoperative complications included the following: operative bleeding requiring transfusion, three patients; prolonged air leak, two patients; death because of hepatic/renal failure, one patient; and death because of overwhelming multisystem aspergillosis, one patient. Seven (54%) patients underwent further immunotoxic treatment with no aspergillosis recurrence. After a mean follow-up of 12 months, five (38%) patients are alive and seven (54%) have died without evidence of aspergillosis and/or mucormycosis.
Conclusions: Surgical resection, in combination with antifungal agents, is a safe and effective form of therapy for invasive mycoses. It prevents recurrence and allows for subsequent cytotoxic therapies.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
White DA, Santamauro JT. Pulmonary infections in immunocompromised patients. Curr Opin Pulm Med 1995;1:202–208.
Denning DW. Therapeutic outcome in invasive aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis 1996;23:608–615.
Kahn FW, Jones JM, Enland DM. The role of bronchoalveolar lavage in the diagnosis of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Am J Clin Pathol 1986;86:518–523.
von Eiff M, Roos N, Schulten R, Hesse M, Zuhlsdorf M, van de Loo J. Pulmonary aspergillosis: early diagnosis improves survival. Respiration 1995;62:341–347.
Denning DW. Invasive aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis 1998;26:781–805.
Hinson KFW, Moon AJ, Plummer NS. Bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: review and report of eight cases. Thorax 1952;7:317–33.
Albelda SM, Talbot GH, Gerson SL. Pulmonary cavitation and massive hemoptysis in invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with acute leukemia. Am J Med 1985;79:57–64.
Pagano L, Ricci P, Nosari A. Fatal haemoptysis in pulmonary filamentous mycosis: an underevaluated cause of death in patients with acute leukaemia in hematological complete remission: a retrospective study and review of literature. Br J Haematol 1995;89:500–505
Gerson SI, Talbot GH, Hurwitz S, Strom BL, Lusk EJ, Casileth PA. Prolonged granulocytopenia: the major risk factor for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with acute leukemia. Ann Intern Med 1984;100:345–351.
Robinson LA, Reed EC, Galbraith TA, Alonso A, Moulton AL, Fleming WH. Pulmonary resection for invasive aspergillus infections in immunocompromised patients. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1995;109:1182–1197.
Baron O, Guillaume B, Moreau P, et al. Aggressive surgical management in localized pulmonary mycotic and nonmycotic infections for neutropenic patients with acute leukemia: report of eighteen cases. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1998;115:63–69.
Reichenberger F, Habicht J, Kaim A, et al. Lung resection for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in neutropenic patients with hematologic diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998;158:885–890.
Caillot D, Casasnovas O, Bernard A, et al. Improved management of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in neutropenic patients using early thoracic computed tomographic scan and surgery. J Clin Oncol 1997;15:139–147.
Kuhlman JE, Fishman EK, Burch PA, Karp JE, Zerhouni EA, Siegelman SS. CT of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. AJR 1988; 150:1015–1020.
Hruban RH, Meziane MA, Zerhouni EA, Wheeler PS, Dumler JS, Hutchins GM. Radiologic-pathologic correlation of the CT halo sign in invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1987;11:534–536.
Robertson MJ, Larson RA. Recurrent fungal pneumonias in patients with acute leukemia undergoing multiple courses of intensive chemotherapy. Am J Med 1988;87:233–239.
Liles WC, Huang JE, van Burik JA, Bowden RA, Da;e DC. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor administered in vivo augments neutrophil activity against opportunistic fungal pathogens. J Infect Dis 1997;175:1012–1015.
Denning DW, Marinus A, Cohen J, et al. An EORTC multicentre prospective survey of invasive aspergillosis in haematologic patients: diagnosis and therapeutic outcome: EORTC Invasive Fungal Infections Cooperative Group. J Infect 1998;37:173–180.
Moreau P, Jahar JR, Milpied N, et al. Localized invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with neutropenia. Cancer 1993;72: 3223–3226.
Bernard A, Caillot D, Couaillier JF, Casasnovas O, Guy H, Favre JP. Surgical management of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in neutropenic patients. Ann Thorac Surg 1997;64:1441–1447.
Salerno CT, Ouyang DW, Pederson TS, et al. Surgical therapy for pulmonary aspergillosis in immunocompromised patients. Ann Thorac Surg 1998;65:1415–1419.
Pagano L, Ricci P, Tonso A, et al. Mucormycosis in patients with haematological malignancies: a retrospective study of 37 cases. Br J Haematol 1997;99:331–336.
Tedder M, Spratt JA, Anstadt MP, Hedge SS, Tedder SD, Lowe JE. Pulmonary mucormycosis: results of medical and surgical therapy. Ann Thorac Surg 1994;57:1044–1050.
Wingard JR, Mellits ED, Sostrin MB, et al. Interstitial pneumonitis after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: nine-year experience at a single institution. Medicine (Baltimore) 1988;67:175–186.
Husni RN, Gordon SM, Longworth DL, et al. Cytomegalovirus infection is a risk factor for invasive aspergillosis in lung transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis 1998;26:753–755.
Peterson PK, McGlave P, Ramsay NKC. A prospective study of infectious diseases following bone marrow transplantation: emergence of aspergillus and cytomegalovirus as the major causes of mortality. Infect Control 1983;4:81–89.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pidhorecky, I., Urschel, J. & Anderson, T. Resection of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Immunocompromised Patients. Ann Surg Oncol 7, 312–317 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10434-000-0312-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10434-000-0312-6