Abstract
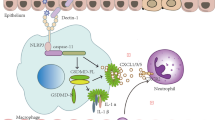
Airway epithelial cells are the first cells to be challenged upon contact with the conidia of Aspergillus. In response, they express pattern-recognition receptors that play fundamental roles as sentinels and mediators of pulmonary innate immunity. The C-type lectin Dectin-1 is expressed predominantly on the surface of myeloid lineage cells. We examined the induction, regulation, and functions of Dectin-1 in pulmonary epithelial cells by challenging human bronchial epithelial (HBE) cells with A. fumigatus. Inflammatory, antimicrobial peptide genes and reactive oxygen species (ROS) were quantified, with and without knockdown of Dectin-1. We found that A. fumigatus induced the expression of Dectin-1 mRNA and protein in HBE cells in a toll-like receptor (TLR) 2-dependent manner. In addition, A. fumigatus-mediated generation of ROS was dependent on the upregulation of Dectin-1. Moreover, A. fumigatus actively induced the expression of TNFα, GM-CSF, IL8, HBD2, and HBD9. Knockdown of Dectin-1 inhibited TNFα, IL8, HBD2, and HBD9 expression. Hence, Dectin-1 was required for the upregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and antimicrobial peptides. Finally, knockdown of TLR2 significantly inhibited Dectin-1 upregulation. Our results demonstrate the novel induction of Dectin-1 in human bronchial epithelial cells and its critical role in the innate immune response against A. fumigatus in non-phagocytic cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Denning DW, Anderson MJ, Turner G, Latgé JP, Bennett JW (2002) Sequencing the Aspergillus fumigatus genome. Lancet Infect Dis 2:251–253
Kleinberg M (2005) Aspergillosis in the CLEAR outcomes trial: working toward a real-world clinical perspective. Med Mycol 43(Suppl 1):S289–S294
Romani L (2011) Immunity to fungal infections. Nat Rev Immunol 11:275–288
Walsh TJ, Roilides E, Cortez K, Kottilil S, Bailey J, Lyman CA (2005) Control, immunoregulation, and expression of innate pulmonary host defenses against Aspergillus fumigatus. Med Mycol 43(Suppl 1):S165–S172
Bellanger AP, Millon L, Khoufache K, Rivollet D, Bièche I, Laurendeau I et al (2009) Aspergillus fumigatus germ tube growth and not conidia ingestion induces expression of inflammatory mediator genes in the human lung epithelial cell line A549. J Med Microbiol 58:174–179
Zhang Z, Liu R, Noordhoek JA, Kauffman HF (2005) Interaction of airway epithelial cells (A549) with spores and mycelium of Aspergillus fumigatus. J Infect 51:375–382
Tai HY, Tam MF, Chou H, Peng HJ, Su SN, Perng DW et al (2006) Pen ch 13 allergen induces secretion of mediators and degradation of occludin protein of human lung epithelial cells. Allergy 61:382–388
Alekseeva L, Huet D, Féménia F, Mouyna I, Abdelouahab M, Cagna A et al (2009) Inducible expression of beta defensins by human respiratory epithelial cells exposed to Aspergillus fumigatus organisms. BMC Microbiol 9:33
Lee HM, Yuk JM, Shin DM, Jo EK (2009) Dectin-1 is inducible and plays an essential role for mycobacteria-induced innate immune responses in airway epithelial cells. J Clin Immunol 29:795–805
Lee HM, Shin DM, Choi DK, Lee ZW, Kim KH, Yuk JM et al (2009) Innate immune responses to Mycobacterium ulcerans via toll-like receptors and dectin-1 in human keratinocytes. Cell Microbiol 11:678–692
Schorey JS, Lawrence C (2008) The pattern recognition receptor Dectin-1: from fungi to mycobacteria. Curr Drug Targets 9:123–129
Reid DM, Montoya M, Taylor PR, Borrow P, Gordon S, Brown GD et al (2004) Expression of the beta-glucan receptor, Dectin-1, on murine leukocytes in situ correlates with its function in pathogen recognition and reveals potential roles in leukocyte interactions. J Leukoc Biol 76:86–94
Taylor PR, Tsoni SV, Willment JA, Dennehy KM, Rosas M, Findon H et al (2007) Dectin-1 is required for beta-glucan recognition and control of fungal infection. Nat Immunol 8:31–38
Underhill DM (2007) Collaboration between the innate immune receptors dectin-1, TLRs, and Nods. Immunol Rev 219:75–87
Xing Z, Harper R, Anunciacion J, Yang Z, Gao W, Qu B et al (2011) Host immune and apoptotic responses to avian influenza virus H9N2 in human tracheobronchial epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 44:24–33
Hohl TM, Van Epps HL, Rivera A, Morgan LA, Chen PL, Feldmesser M et al (2005) Aspergillus fumigatus triggers inflammatory responses by stage-specific beta-glucan display. PLoS Pathog 1:e30
Mezger M, Kneitz S, Wozniok I, Kurzai O, Einsele H, Loeffler J (2008) Proinflammatory response of immature human dendritic cells is mediated by dectin-1 after exposure to Aspergillus fumigatus germ tubes. J Infect Dis 197:924–931
Xing Z, Conway EM, Kang C, Winoto A (2004) Essential role of survivin, an inhibitor of apoptosis protein, in T cell development, maturation, and homeostasis. J Exp Med 199:69–80
Xing Z, Cardona CJ, Adams S, Yang Z, Li J, Perez D et al (2009) Differential regulation of antiviral and proinflammatory cytokines and suppression of Fas-mediated apoptosis by NS1 of H9N2 avian influenza virus in chicken macrophages. J Gen Virol 90:1109–1118
Ye J, Li J, Yu Y, Wei Q, Deng W, Yu L (2010) L-carnitine attenuates oxidant injury in HK-2 cells via ROS-mitochondria pathway. Regul Pept 161:58–66
Blundell J, Blaiss CA, Etherton MR, Espinosa F, Tabuchi K, Walz C et al (2010) Neuroligin-1 deletion results in impaired spatial memory and increased repetitive behavior. J Neurosci 30:2115–2129
Balloy V, Sallenave JM, Wu Y, Touqui L, Latgé JP, Si-Tahar M et al (2008) Aspergillus fumigatus-induced interleukin-8 synthesis by respiratory epithelial cells is controlled by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, p38 MAPK, and ERK1/2 pathways and not by the toll-like receptor-MyD88 pathway. J Biol Chem 283:30513–30521
Huttunen K, Hyvärinen A, Nevalainen A, Komulainen H, Hirvonen MR (2003) Production of proinflammatory mediators by indoor air bacteria and fungal spores in mouse and human cell lines. Environ Health Perspect 111:85–92
Borger P, Koëter GH, Timmerman JA, Vellenga E, Tomee JF, Kauffman HF (1999) Proteases from Aspergillus fumigatus induce interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-8 production in airway epithelial cell lines by transcriptional mechanisms. J Infect Dis 180:1267–1274
Gantner BN, Simmons RM, Underhill DM (2005) Dectin-1 mediates macrophage recognition of Candida albicans yeast but not filaments. EMBO J 24:1277–1286
Gribar SC, Richardson WM, Sodhi CP, Hackam DJ (2008) No longer an innocent bystander: epithelial toll-like receptor signaling in the development of mucosal inflammation. Mol Med 14:645–659
Herre J, Willment JA, Gordon S, Brown GD (2004) The role of Dectin-1 in antifungal immunity. Crit Rev Immunol 24:193–203
Brown GD, Gordon S (2001) Immune recognition. A new receptor for beta-glucans. Nature 413:36–37
Brown GD, Herre J, Williams DL, Willment JA, Marshall AS, Gordon S (2003) Dectin-1 mediates the biological effects of beta-glucans. J Exp Med 197:1119–1124
Ariizumi K, Shen GL, Shikano S, Xu S, Ritter R 3rd, Kumamoto T et al (2000) Identification of a novel, dendritic cell-associated molecule, dectin-1, by subtractive cDNA cloning. J Biol Chem 275:20157–20167
Taylor PR, Brown GD, Reid DM, Willment JA, Martinez-Pomares L, Gordon S et al (2002) The beta-glucan receptor, dectin-1, is predominantly expressed on the surface of cells of the monocyte/macrophage and neutrophil lineages. J Immunol 169:3876–3882
Cunha C, Di Ianni M, Bozza S, Giovannini G, Zagarella S, Zelante T et al (2010) Dectin-1 Y238X polymorphism associates with susceptibility to invasive aspergillosis in hematopoietic transplantation through impairment of both recipient- and donor-dependent mechanisms of antifungal immunity. Blood 116:5394–5402
Dagenais TR, Keller NP (2009) Pathogenesis of Aspergillus fumigatus in invasive Aspergillosis. Clin Microbiol Rev 22:447–465
Dagenais TR, Giles SS, Aimanianda V, Latgé JP, Hull CM, Keller NP (2010) Aspergillus fumigatus LaeA-mediated phagocytosis is associated with a decreased hydrophobin layer. Infect Immun 78:823–829
Paris S, Debeaupuis JP, Crameri R, Carey M, Charlès F, Prévost MC et al (2003) Conidial hydrophobins of Aspergillus fumigatus. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1581–1588
Akira S, Takeda K (2004) Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 4:499–511
Han X, Yu R, Zhen D, Tao S, Schmidt M, Han L (2011) Beta-1,3-Glucan-induced host phospholipase D activation is involved in Aspergillus fumigatus internalization into type II human pneumocyte A549 cells. PLoS One 6:e21468
Nathan C (2006) Neutrophils and immunity: challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Immunol 6:173–182
Segal BH, Romani LR (2009) Invasive aspergillosis in chronic granulomatous disease. Med Mycol 47(Suppl 1):S282–S290
Shin DM, Yang CS, Yuk JM, Lee JY, Kim KH, Shin SJ et al (2008) Mycobacterium abscessus activates the macrophage innate immune response via a physical and functional interaction between TLR2 and dectin-1. Cell Microbiol 10:1608–1621
Acknowledgments
This study was granted by the Hospital Foundation of Jinling Hospital (2011026). The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Table 1
Sequences of primers for the real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) (DOCX 12 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, WK., Lu, X., Li, X. et al. Dectin-1 is inducible and plays a crucial role in Aspergillus-induced innate immune responses in human bronchial epithelial cells. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 31, 2755–2764 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-012-1624-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-012-1624-8