Abstract
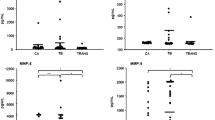
The angiogenesis system has been implicated in inflammatory and neoplastic processes; nevertheless, it has been little studied in relation to the pleural space. Our aim is to analyze pleural and plasma levels of the activators-vascular endothelial growth factor, basic fibroblastic growth factor, and inhibitors-endostatin and thrombospondin-1 and to estimate the association between these factors and related biochemical markers. We analyzed pleural fluid from 105 patients with one of the following types of pleural effusion: empyema or complicated parapneumonic, non-complicated parapneumonic, tuberculous, neoplastic and transudative. Angiogenesis activators were higher in exudates than in transudates (p < 0.001) and in empyema than in non-complicated parapneumonic patients (p < 0.001). Endostatin showed no significant differences. Trombospondin-1 showed higher levels in exudates than in transudates and in empyema than in non-complicated parapneumonic effusions (p < 0.001). In pleural exudates there was a positive correlation of angiogenesis activators and trombospondin-1 with low glucose and pH and high LDH. There was no correlation between pleural and plasma levels of the angiogenesis factors. We conclude that exudative pleural effusions showed higher vascular endothelial growth factor, basic-fibroblastic growth factor and trombospondin-1 values than transudative effusions -that associated to low glucose and pH, and high LDH. There was no correlation between pleural and plasma concentrations, suggesting a compartmentalized response.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
InstitutionalAuthorNameRuckdeschel JC (1995) ArticleTitleManagement of malignant pleural effusions Seminars Oncology 22 58–63
InstitutionalAuthorNameJurado Gámez B (1997) ArticleTitleNeumonia y derrame pleural. Manejo terapeutico An Med Interna (Madrid) 14 419–424
VB Antony SA Sahn B Mossman DB Gail A Kalica (1992) ArticleTitlePleural cell biology in health and disease Am Rev Respir Dis 145 1236–1239 Occurrence Handle1586074
C Kroegel VB Antony (1997) ArticleTitleImmunobiology of pleural inflammation: potential implications for pathogenesis, diagnosis and therapy Eur Respir J 10 2411–2418 Occurrence Handle10.1183/09031936.97.10102411 Occurrence Handle9387973
VB Antony K Mohammed (1999) ArticleTitlePathophysiology of pleural space infections Semin Respir Infect 14 9–17 Occurrence Handle10197393
KA Mohhamed N Nasreen J Hardwick et al. (2001) ArticleTitleBacterial induction of pleural mesothelial monolayer barrier dysfunction Am J Phisiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 281 L119–L125
DR Thickett L Armstrong AB Millar (1999) ArticleTitleVascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in inflammatory and malignant pleural effusions Thorax 54 707–710 Occurrence Handle10413724
CS Grove YC Gary Lee (2002) ArticleTitleVascular endothelial growth factor: the key mediator in pleural effusion formation Curr Opin Pulm Med 8 294–301 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00063198-200207000-00009 Occurrence Handle12055392
P Carmeliet (2001) ArticleTitleClotting factors build blood vessels Science 293 1602–1604 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.1064981 Occurrence Handle11533466
J Folkman Y Shing (1992) ArticleTitleAngiogenesis J Biol Chem 267 10931–10934 Occurrence Handle1375931
J Folkman (1995) ArticleTitleClinical applications of research on angiogenesis N Engl J Med 333 1757–1763 Occurrence Handle10.1056/NEJM199512283332608 Occurrence Handle7491141
D Hanahan J Folkman (1996) ArticleTitlePatterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis Cell 86 353–364 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80108-7 Occurrence Handle8756718
W Risau (1997) ArticleTitleMechanisms of angiogenesis Nature 386 671–674 Occurrence Handle10.1038/386671a0 Occurrence Handle9109485
F Bussolino A Mantovani G Persico (1997) ArticleTitleMolecular mechanisms of blood vessel formation TIBS 22 251–256 Occurrence Handle9255066
ML Iruela-Arispe HF Dvorak (1997) ArticleTitleAngiogenesis: a dynamic balance of stimulators and inhibitors Thromb and Haemost 78 672–677
O Ishimoto Y Saijo K Narumi (2002) ArticleTitleHigh level of vascular endothelial growth factor in hemorrhagic pleural effusion of cancer Oncology 63 70–75 Occurrence Handle10.1159/000065723 Occurrence Handle12187074
JC Adams (1997) ArticleTitleMolecules in focus. Thrombospondin-1 Int J Biochem Cell Biol 29 861–865 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1357-2725(96)00171-9 Occurrence Handle9304800
MS O’Reilly T Boehm Y Shing et al. (1997) ArticleTitleEndostatin: an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor growth Cell 88 277–285 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81848-6 Occurrence Handle9008168
M Sumi K Kagohashi H Satoh H Ishikawa Y Funayama K Sekizawa (2003) ArticleTitleEndostatin levels in exudative pleural effurfsions Lung 181 329–334 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00408-003-1035-9 Occurrence Handle14749937
RW Light WM Girard SG Jenkinson RB George (1980) ArticleTitleParapneumonic effusions Am J Med 69 507–511 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0002-9343(80)90460-X Occurrence Handle7424940
I Ocaña JM Martínez-Vázquez RM Segura T Fernández Sevilla Particlede JA Capdevila (1983) ArticleTitleAdenosine deaminase in pleural fluids: test for diagnosis of tuberculous pleural effusion Chest 84 51–53 Occurrence Handle6602695
SA Sahn (1987) ArticleTitleMalignant pleural effusion Semin Respir Med 9 43–53
RW Light MI MacGregor PC Luchsinger WC Ball (1972) ArticleTitlePleural effusions: diagnostic separation of transudates and exudates An Intern Med 77 507–513
B Wang Q Wiong Q Shi D Tan X Le K Xie (2001) ArticleTitleGenetic disruption of host nitric oxide synthase II gene impairs melanoma-induced angiogenesis and suppresses pleural effusion Int J Cancer 91 607–6011 Occurrence Handle10.1002/1097-0215(200002)9999:9999<::AID-IJC1109>3.3.CO;2-4 Occurrence Handle11267968
SA Milligan MW Owens MB Grisham (1996) ArticleTitleAugmentation of cytokine-induced nitric-oxide synthesis by hydrogen peroxide Am J Physiol 271 114–120
D D’Arcangelo F Facchiano LM Barlucchi et al. (2000) ArticleTitleAcidosis inhibits endothelial cell apoptosis and function and induces basic fibroblastic growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor expression Circ Res 86 312–318 Occurrence Handle10679483
H Yanagawa E Takeuchi Y Suzuki Y Ohmoto H Bando S Sone (1999) ArticleTitleVascular endothelial growth factor in malignant pleural effusion associated with lung cancer Cancer Immunol Immunother 48 396–400 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002620050592 Occurrence Handle10501853
D Cheng RM Rodriguez EA Perkett et al. (1999) ArticleTitleVascular endothelial growth factor in pleural fluid Chest 116 760–765 Occurrence Handle10.1378/chest.116.3.760 Occurrence Handle10492284
JE König E Tolnay T Wiethege KM Müller (2000) ArticleTitleCo-expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor flt-1 in malignant pleural mesothelioma Respiration 67 36–40 Occurrence Handle10.1159/000029460 Occurrence Handle10705260
Strizzi b A Catalano G Vianale et al. (2001) ArticleTitleVascular endothelial growth factor is an autocrine growth factor in human malignant mesothelioma J Pathol 193 468–475 Occurrence Handle10.1002/path.824 Occurrence Handle11276005
KT Yeo HH Wang JA Nagy et al. (1993) ArticleTitleVascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) in guinea pig and human tumor and inflammatory effusions Cancer Res 53 2912–2918 Occurrence Handle8504432
A Kraft K Weindel A Ochs C Marth et al. (1999) ArticleTitleVascular endothelial growth factor in the sera and effusions of patients with malignant and nonmalignant disease Cancer 85 178–187 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19990101)85:1<178::AID-CNCR25>3.0.CO;2-7 Occurrence Handle9921991
BK Zebrowski S Yano W Liu (1999) ArticleTitleVascular endothelial growth factor levels and induction of permeability in malignant pleural effusions Clin Cancer Res 5 3364–3368 Occurrence Handle10589746
Y Aoki G Tosato (2001) ArticleTitleVascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor in the pathogenesis of primary effusion lymphomas Leuk Lymphoma 41 229–237 Occurrence Handle11378536
L Strizzi G Vianale A Catalano R Muraro L Mutti A Procopio (2001) ArticleTitleBasic fibroblast growth factor in mesothelioma pleural effusions correlation with patient survival and angiogenesis Int J Oncol 18 1093–1098 Occurrence Handle11295061
H Momi W Matsuyama K Inoue et al. (2002) ArticleTitleVascular endothelial growth factor and proinflammatory cytokines in pleural effusions Respir Med 96 817–822 Occurrence Handle10.1053/rmed.2002.1364 Occurrence Handle12412982
EA Hamed AM EI-Noweihi AZ Mohamed A Mahmoud (2004) ArticleTitleVasoactive mediators (VEGF and TNF-alpha) in patients with malignant and tuberculous pleural effusions Respirology 9 81–86 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1440-1843.2003.00529.x Occurrence Handle14982607
ML Iruela-Arispe P Porter P Bornstein EH Sage (1996) ArticleTitleThrombospondin-1, an inhibitor of angiogenesis, is regulated by progesterone in the human endometrium J Clin Invest 97 403–412 Occurrence Handle8567961
LA DiPietro DR Nebgen PJ Polverini (1994) ArticleTitleDownregulation of endothelial cell thrombospondin 1 enhances in vitro angiogenesis J Vasc Res 31 178–185 Occurrence Handle7511943
SS Tolsma OV Volpert DJ Good WA Frazier PJ Polverini N Bouck (1993) ArticleTitlePeptides derived from two separate domains of the matrix protein thrombospondin 1 have anti-angiogenic activity J Cell Biol 122 497–511 Occurrence Handle10.1083/jcb.122.2.497 Occurrence Handle7686555
JC Adams (1997) ArticleTitleMolecules in focus. Thrombospondin-1 Int J Biochem Cell Biol 29 861–865 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1357-2725(96)00171-9 Occurrence Handle9304800
D Albo DH Berger TN Wang X Hu V Rothman GP Tuszynski (1997) ArticleTitleThrombospondin-1 and transforming growth factor-beta 1 promote breast tumor cell invasion through up-regulation of the plasminogen/plasmin system Surgery 122 493–500 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0039-6060(97)90043-X Occurrence Handle9288157
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Olga Merino, nursing supervisor, Francisco Vivas and Pilar Gutierrez, nurses, for their participation. They also thank Celine Carvallo for linguistic advice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported in part by FIS Grant 01/1408
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruiz, E., Alemán, C., Alegre, J. et al. Angiogenic Factors and Angiogenesis Inhibitors in Exudative Pleural Effusions. Lung 183, 185–195 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-004-2533-0
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-004-2533-0