Abstract
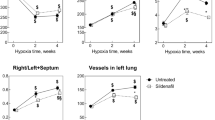
The present study aimed to investigate the effects of olmesartan, an antagonist for angiotensin II receptor type 1(AT1), on the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK)1/2, tissue remodeling, and pro-inflammatory signals in the right ventricle and lung of mice during the early phase of hypobaric hypoxia. Phosphorylation of ERK1/2 in both tissue types in response to hypoxia peaked at 1–3 days, and declined rapidly in the right ventricle, whereas in the lung it was sustained for at least 8 days. Upregulation of angiotensinogen mRNA was observed in the hypoxic lung at 4–9 days, but not in the hypoxic right ventricle and pulmonary artery. Olmesartan inhibited the hypoxia-induced phosphorylation of ERK1/2 in the lung, but not in the right ventricle. Neither right ventricular hypertrophy nor the thickening of the intrapulmonary arterial wall was ameliorated by olmesartan. However, this drug inhibited the expression of the mRNA for angiotensinogen and several pro-inflammatory factors, including interleukin-6 and inducible nitric oxide synthase in the hypoxic lung. These results suggest that olmesartan blocks a potential positive feedback loop of the angiotensin II-AT1 receptor system, which may lead to attenuate pro-inflammatory signals in the mouse lung, that are associated with hypoxic pulmonary hypertension, without inducing any appreciable effects on the compensatory cardiopulmonary hypertrophy at an early phase of exposure to a hypobaric hypoxic environment.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACE:
-
angiotensin-converting enzyme
- Ang:
-
angiotensinogen
- Ang II:
-
angiotensin II
- AT1 and AT2:
-
Ang II receptor types 1 and 2
- CMC:
-
carboxymethylcellulose
- COX:
-
cyclooxygenase
- ERK:
-
extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase
- GAPDH:
-
glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- HO-1:
-
heme oxygenase-1
- IL-6:
-
interleukin 6
- iNOS:
-
inducible nitric oxide synthase
- KC:
-
keratinocyte-derived chemokines
- MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MCP:
-
monocyte chemoattractant protein
- MEK:
-
MAPK/ERK kinase
- MIP:
-
macrophage inflammatory protein
- PDGFR:
-
platelet-derived growth factor receptor
- RT-PCR:
-
reverse-transcription and polymerase chain reaction
- TNF-α:
-
tumor necrosis factor-α
References
Adamy C, Oliviero P, Eddahibi S, Rappaport L, Samuel JL, Teiger E, Chassagne C (2002) Cardiac modulations of ANG II receptor expression in rats with hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 283:H733–H740
Bhargava A, Kumar A, Yuan N, Gewitz MH, Mathew R (1999) Monocrotaline induces interleukin-6 mRNA expression in rat lungs. Heart Dis 1:126–132
Brasier AR, Recinos A III, Eledrisi MS (2002) Vascular inflammation and the renin-angiotensin system. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 22:1257–1266
Campian ME, Hardziyenka M, Michel MC, Tan HL (2006) How valid are animal models to evaluate treatments for pulmonary hypertension? Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol [Published online: 24 August 2006] DOI 10.1007/s00210-006-0087-9
Chassagne C, Eddahibi S, Adamy C, Rideau D, Marotte F, Dubois-Rande JL, Adnot S, Samuel JL, Teiger E (2000) Modulation of angiotensin II receptor expression during development and regression of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 22:323–332
Cheng TH, Liu JC, Lin H, Shih NL, Chen YL, Huang MT, Chan P, Cheng CF, Chen JJ (2004) Inhibitory effect of resveratrol on angiotensin II-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 369:239–244
Clozel JP, Saunier C, Hartemann D, Fischli W (1991) Effects of cilazapril, a novel angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor, on the structure of pulmonary arteries of rats exposed to chronic hypoxia. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 17:36–40
Deindl E, Kolar F, Neubauer E, Vogel S, Schaper W, Ostadal B (2003) Effect of intermittent high altitude hypoxia on gene expression in rat heart and lung. Physiol Res 52:147–157
Eguchi S, Dempsey PJ, Frank GD, Motley ED, Inagami T (2001) Activation of MAPKs by angiotensin II in vascular smooth muscle cells. Metalloprotease-dependent EGF receptor activation is required for activation of ERK and p38 MAPK but not for JNK. J Biol Chem 276:7957–7962
Fulton RM, Hutchinson EC, Jones AM (1952) Ventricular weight in cardiac hypertrophy. Br Heart J 14:413–420
Fung YC, Liu SQ (1991) Changes of zero-stress state of rat pulmonary arteries in hypoxic hypertension. J Appl Physiol 70:2455–2470
Hampl V, Herget J (2000) Role of nitric oxide in the pathogenesis of chronic pulmonary hypertension. Physiol Rev 80:1337–1372
Hirano T (1998) Interleukin 6 and its receptor: ten years later. Int Rev Immunol 16:249–284
Hoshikawa Y, Nana-Sinkam P, Moore MD, Sotto-Santiago S, Phang T, Keith RL, Morris KG, Kondo T, Tuder RM, Voelkel NF, Geraci MW (2003) Hypoxia induces different genes in the lungs of rats compared with mice. Physiol Genomics 12:209–219
Humbert M, Monti G, Brenot F, Sitbon O, Portier A, Grangeot-Keros L, Duroux P, Galanaud P, Simonneau G, Emilie D (1995) Increased interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 serum concentrations in severe primary pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 151:1628–1631
Jackson CL, Schwartz SM (1992) Pharmacology of smooth muscle cell replication. Hypertension 20:713–736
Jeffery TK, Morrell NW (2002) Molecular and cellular basis of pulmonary vascular remodeling in pulmonary hypertension. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 45:173–202
Jeffery TK, Wanstall JC (1999) Perindopril, an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor, in pulmonary hypertensive rats: comparative effects on pulmonary vascular structure and function. Br J Pharmacol 128:1407–1418
Karamsetty VS, Kane KA, Wadsworth RM (1995) The effects of chronic hypoxia on the pharmacological responsiveness of the pulmonary artery. Pharmacol Ther 68:233–246
Katayose D, Isoyama S, Fujita H, Shibahara S (1993) Separate regulation of heme oxygenase and heat shock protein 70 mRNA expression in the rat heart by hemodynamic stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 191:587–594
Kentera D, Susic D, Cvetkovic A, Djordjevic G (1981) Effects of SQ 14.225, an orally active inhibitor of angiotensin-converting enzyme, on hypoxic pulmonary hypertension and right ventricular hypertrophy in rats. Basic Res Cardiol 76:344–351
Kudoh S, Komuro I, Hiroi Y, Zou Y, Harada K, Sugaya T, Takekoshi N, Murakami K, Kadowaki T, Yazaki Y (1998) Mechanical stretch induces hypertrophic responses in cardiac myocytes of angiotensin II type 1a receptor knockout mice. J Biol Chem 273:24037–24043
Madjdpour C, Jewell UR, Kneller S, Ziegler U, Schwendener R, Booy C, Klausli L, Pasch T, Schimmer RC, Beck-Schimmer B (2003) Decreased alveolar oxygen induces lung inflammation. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 284:L360–367
Meyrick B, Reid L (1978) The effect of continued hypoxia on rat pulmonary arterial circulation. An ultrastructural study. Lab Invest 38:188–200
Meyrick B, Reid L (1979) Hypoxia and incorporation of 3H-thymidine by cells of the rat pulmonary arteries and alveolar wall. Am J Pathol 96:51–70
Meyrick B, Reid L (1980) Hypoxia-induced structural changes in the media and adventitia of the rat hilar pulmonary artery and their regression. Am J Pathol 100:151–178
Minamino T, Christou H, Hsieh CM, Liu Y, Dhawan V, Abraham NG, Perrella MA, Mitsialis SA, Kourembanas S (2001) Targeted expression of heme oxygenase-1 prevents the pulmonary inflammatory and vascular responses to hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:8798–8803
Miyata M, Sakuma F, Yoshimura A, Ishikawa H, Nishimaki T, Kasukawa R (1995) Pulmonary hypertension in rats. 2. Role of interleukin-6. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 108:287–291
Miyata M, Ito M, Sasajima T, Ohira H, Kasukawa R (2001) Effect of a serotonin receptor antagonist on interleukin-6-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. Chest 119:554–561
Mizuno M, Sada T, Ikeda M, Fukuda N, Miyamoto M, Yanagisawa H, Koike H (1995) Pharmacology of CS-866, a novel nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol 285:181–188
Morrell NW, Morris KG, Stenmark KR (1995) Role of angiotensin-converting enzyme and angiotensin II in development of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Am J Physiol 269:H1186–H1194
Morrell NW, Upton PD, Kotecha S, Huntley A, Yacoub MH, Polak JM, Wharton J (1999) Angiotensin II activates MAPK and stimulates growth of human pulmonary artery smooth muscle via AT1 receptors. Am J Physiol 277:L440–L448
Nakamoto T, Harasawa H, Akimoto K, Hirata H, Kaneko H, Kaneko N, Sorimachi K (2005) Effects of olmesartan medoxomil as an angiotensin II-receptor blocker in chronic hypoxic rats. Eur J Pharmacol 528:43–51
Nakayama K, Fukuta Y, Kiyoshi A, Iwatsuki Y, Ishii K, Ishikawa T, Iida M, Iwata H, Enomoto M (1999) (+)−[3H]isradipine and [3H]glyburide bindings to heart and lung membranes from rats with monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension. Jpn J Pharmacol 81:176–184
Nong Z, Stassen JM, Moons L, Collen D, Janssens S (1996) Inhibition of tissue angiotensin-converting enzyme with quinapril reduces hypoxic pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary vascular remodeling. Circulation 94:1941–1947
Pearson G, Robinson F, Beers Gibson T, Xu BE, Karandikar M, Berman K, Cobb MH (2001) Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: regulation and physiological functions. Endocr Rev 22:153–183
Pelouch V, Kolar F, Ost’adal B, Milerova M, Cihak R, Widimsky J (1997) Regression of chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension, right ventricular hypertrophy, and fibrosis: effect of enalapril. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 11:177–185
Rhodes J (2005) Comparative physiology of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension: historical clues from brisket disease. J Appl Physiol 98:1092–1100
Rumsey WL, Abbott B, Bertelsen D, Mallamaci M, Hagan K, Nelson D, Erecinska M (1999) Adaptation to hypoxia alters energy metabolism in rat heart. Am J Physiol 276:H71–H80
Saito Y, Haendeler J, Hojo Y, Yamamoto K, Berk BC (2001) Receptor heterodimerization: essential mechanism for platelet-derived growth factor-induced epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation. Mol Cell Biol 21:6387–6394
Schermuly RT, Dony E, Ghofrani HA, Pullamsetti S, Savai R, Roth M, Sydykov A, Lai YJ, Weissmann N, Seeger W, Grimminger F (2005) Reversal of experimental pulmonary hypertension by PDGF inhibition. J Clin Invest 115:2811–2821
Schultz Jel J, Witt SA, Glascock BJ, Nieman ML, Reiser PJ, Nix SL, Kimball TR, Doetschman T (2002) TGF-β 1 mediates the hypertrophic cardiomyocyte growth induced by angiotensin II. J Clin Invest 109:787–796
Seta K, Nanamori M, Modrall JG, Neubig RR, Sadoshima J (2002) AT1 receptor mutant lacking heterotrimeric G protein coupling activates the Src-Ras-ERK pathway without nuclear translocation of ERKs. J Biol Chem 277:9268–9277
Sharma S, Taegtmeyer H, Adrogue J, Razeghi P, Sen S, Ngumbela K, Essop MF (2004) Dynamic changes of gene expression in hypoxia-induced right ventricular hypertrophy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 286:H1185–1192
Sinn PL, Zhang X, Sigmund CD (1999) JG cell expression and partial regulation of a human renin genomic transgene driven by a minimal renin promoter. Am J Physiol 277:F634–F642
Sugino H, Ozono R, Kurisu S, Matsuura H, Ishida M, Oshima T, Kambe M, Teranishi Y, Masaki H, Matsubara H (2001) Apoptosis is not increased in myocardium overexpressing type 2 angiotensin II receptor in transgenic mice. Hypertension 37:1394–1398
Tanabe Y, Saito M, Ueno A, Nakamura M, Takeishi K, Nakayama K (2000) Mechanical stretch augments PDGF receptor β expression and protein tyrosine phosphorylation in pulmonary artery tissue and smooth muscle cells. Mol Cell Biochem 215:103–113
Tuder RM, Voelkel NF (1998) Pulmonary hypertension and inflammation. J Lab Clin Med 132:16–24
van Suylen RJ, Aartsen WM, Smits JF, Daemen MJ (2001) Dissociation of pulmonary vascular remodeling and right ventricular pressure in tissue angiotensin-converting enzyme-deficient mice under conditions of chronic alveolar hypoxia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 163:1241–1245
Voelkel NF, Tuder RM (2000) Hypoxia-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling: a model for what human disease? J Clin Invest 106:733–738
Zakheim RM, Mattioli L, Molteni A, Mullis KB, Bartley J (1975) Prevention of pulmonary vascular changes of chronic alveolar hypoxia by inhibition of angiotensin I-converting enzyme in the rat. Lab Invest 33:57–61
Zhao L, al-Tubuly R, Sebkhi A, Owji AA, Nunez DJ, Wilkins MR (1996) Angiotensin II receptor expression and inhibition in the chronically hypoxic rat lung. Br J Pharmacol 119:1217–1222
Zielinski J (2005) Effects of intermittent hypoxia on pulmonary haemodynamics: animal models versus studies in humans. Eur Respir J 25:173–180
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Sankyo, for providing us with the olmesartan. We are also grateful to Mr. Y. Okamoto, Ms. K. Sato, and Mr. T. Kitayama for their technical assistance with the animal handling. This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) (14572059) from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports, and Culture of Japan from 2002–2004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanabe, Y., Morikawa, Y., Kato, T. et al. Effects of olmesartan, an AT1 receptor antagonist, on hypoxia-induced activation of ERK1/2 and pro-inflammatory signals in the mouse lung. Naunyn-Schmied Arch Pharmacol 374, 235–248 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-006-0110-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-006-0110-1