Abstract
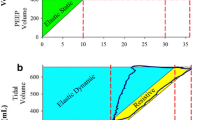
A comparison is made of the linear and non-linear least squares characterizations of the relationship between the transthoracic impedance change (ΔZ) and the respired air volume (ΔV) with regard to electrode location, somatotype, body position and type of breathing for seven normal, male, human subjects. The electrode locations which provided the largest ΔZ signal and those which produced the least error in the values of ΔV as determined from the measured values of ΔZ were also studied.
Sommaire
On fait une comparison des caractéristiques linéaires et non-linéaires par la méthode des moindres carrés des relations entre les variations d'impédance transthoracique (ΔZ) et le volume d'air respiré (ΔV) en tenant compte de la position des électrodes, du somatotype, de la position du corps et du type de respiration sur sept sujets humains normaux. Les positions des électrodes qui fournissent le plus grand ΔZ et celles qui produisent l'erreur moindre dans les valeurs de ΔV, déterminées d'après les valeurs mésurées de ΔZ, sont aussi étudiées.
Zusammenfassung
Ein Vergleich wird angestellt zwischen der linearen und der nichtlinearen Darstellung (Methode der kleinsten Fehlerquadrate) der Beziehung zwischen der transthorakalen Impedanzänderung ΔZ und dem Atemvolumen ΔV bezüglich Elektrodenlokalisation, Somatotyp, Körperlage und Atemtyp bei sieben normalen männlichen Versuchspersonen. Die Elektrodenlokalisationen wurden untersucht, welche das größte ΔZ-Signal ergaben, und die jenigen, welche nach Ausrechnung aus den gemessenen ΔZ-Werten den kleinsten Fehler in den ΔV-Werten ergaben.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison, R. D. (1962) Volumetric dynamics of respiration as measured by electrical impedance plethysmography. Ph. D. Thesis. Wayne State University. Detroit, Michigan.
Allison, R. D., Holmes, E. L. andNyboer, J. (1964) Volumetric dynamics of respiration as measured by electrical impedance plethysmography.J. appl. Physiol.,19, 166–173.
Atzler, E., undLehmann, G. (1932) Über ein neues Verfahren zur Darstellung der Herztätigkeit (Dielektrographie).Arbeitsphysiologie,4, 636.
Atzler, E. (1935) Dielektrographie. InHandbuch der Biologischen Arbeitsmethoden. pp. 1073–1084. Urban und Schwarzenberg. Berlin-Wein.
Ax, A. F., Andreski, L., Courter, R., Di Giovanni, C., Herman, S., Lucas, D. andOrrick, W. (1964) Measurement of Human Respiration by Telemeter Impedance, Strain Gage and Spirometer. Presented at the Instrument Society of America. 2nd National Biomedical Sciences Instrumentation Symposium. Albuquerque, New Mexico. May, 1964.
Baker, L. E., Geddes, L. A. andHoff, H. E. (1965) Quantitative evaluation of impedance spirometry in man.Am. J. med. Electron.,4, 73–77.
Berry, C. A., Minners, H. A., McCutcheon, E. P. andPollard, R. A. (1962) NASA SP-12. Results of the Third United States Manned Orbital Space Flight October 3, 1962. pp. 23–37 (120 pp). Office of Scientific and Technical Information, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Washington, D.C.
Catterson, A. D., McCutcheon, E. P., Minners, H. A. andPollard, R. A. (1963) NASA SP-45. Mercury Project Summary, including Results of the Fourth Manned Orbital Flight May 15 and 16, 1963. pp. 299–326 (444 pp). Office of Scientific and Technica Information. National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Washington, D.C.
Geddes, L. A., Hoff, H. E., Hickman, D. M. andMoore A. G. (1962) The impedance pneumograph.Aerospace Med.,33, 28–33.
Geddes, L. A. andHoff, H. E. (1962) Hales, Marey and Chauveau, Annual Report HTS 5125 (60 pp). National Heart Institute, Washington, D.C.
Geddes, L. A., Hoff, H. E., Spencer, W. A. andVallbona, C. (1962) Acquisition of physiological data at the bedside.Am. J. med. Electron.,1, 62–70.
Geddes, L. A., Hoff, H. E. andSpencer, W. A. (1964) Monitoring patients in hospitals—An exercise in automation.The Slide Rule.,24 4–7.
Goldensohn, R. A. andZablow, L. (1959) An electrical spirometer.J. appl. Physiol. 14, 463–464.
Guillemin, E. A. (1949) InThe Mathematics of Circuit Analysis, pp. 64–68 (590 pp). John Wiley, New York.
Hamilton, L. H., Beard, J. D. andKory, R. C. (1965) Impedance measurement of tidal volume and ventilation.J. appl. Physiol. 20, 565–568.
Hanish, H. M. (1962) Telemetry of respiration and the electrocardiogram from the same pair of electrodes. 15th Annual Conference on Engineering in Medicine and Biology. p. 39 (66 pp). Carl Gorr, Chicago.
Kinnen, E., Kubicek, W. andTurton, G. (1963) Thoracic cage impedance measurements. Dynamic characteristics of an impedance pneumograph Tech. Documentary Rep. No. SAM-TDR-63-100. USAF. School of Aerospace Medicine, Brooks Air Force Base, Texas.
Kubicek, W., Kinnen, E. andEdin, A. (1963) Thoracic cage impedance measurements. Calibration of an impedance pneumograph. Tech. Documentary Rep. No. SAM-TDR-63-41. USAF School of Aerospace Medicine, Brooks Air Force Base, Texas.
Kubicek, W., Kinnen, E. andEdin, A. (1964) Calibration of an impedance pneumograph.J. appl. Physiol.,18, 557–560.
McCally, M., Barnard, G. W., Robins, K. E. andMarko, A. R. (1963) Observations with an electrical impedance respirometer.Am. J. med. Electron.,2, 322–327.
Nyboer, J. (1959) InElectrical Impedance Plethysmography. p. 122 (243 pp). Thomas, Springfield Illinois.
Pallett, J. E. andScopes, J. W. (1965) Recording respirations in newborn babies by measuring impedance of the chest.Med. Electron. biol. Engng.,3, 161–168.
Robbins, K. E. andMarko, A. (1962) An improved method of registering respiration rate. 15th Annual Conference on Engineering in Medicine and Biology. p. 18 (66 pp). Carl Gorr, Chicago.
Schaefer, H., Bleicher, E. andEckervogt, F. (1949) Weitere Beitärge zur Electrischen Reizung und zur Registrierung von Elektrischen Vorgängen und der Atmung.Pflügers. Arch. ges. Physiol.,251, 491–503.
Spiegel, M. R. (1961) InSchaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Statistics. p. 221 (359 pp). Schaum, New York.
Vallbona, C., Geddes, L. A., Harrison, G. M., Hoff, H. E. andSpencer, W. A. (1965) Physiological Monitor: Experience, Clinical Value and Problems. Proceedings of the 1965 National Telemetering Conference, Instrument Society of America. pp. 126–129 (228 pp). Lewis Winner, New York. Library of Congress Card No. 57-20724.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Biophysics Development Fund, Dept. of Physiology.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baker, L.E., Geddes, L.A. & Hoff, H.E. A comparison of linear and non-linear characterizations of impedance spirometry data. Med. & biol. Engng. 4, 371–379 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02476155
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02476155