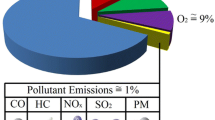
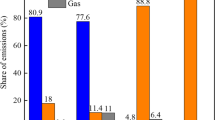
Summary
Since the use of diesel engines is still increasing, the contribution of their incomplete combustion products to air pollution is becoming ever more important. The presence of irritating and genotoxic substances in both the gas phase and the particulate phase constituents is considered to have significant health implications. The quantity of soot particles and the particle-associated organics emitted from the tail pipe of a diesel-powered vehicle depend primarily on the engine type and combustion conditions but also on fuel properties. The quantity of soot particles in the emissions is determined by the balance between the rate of formation and subsequent oxidation. Organics are adsorbed onto carbon cores in the cylinder, in the exhaust system, in the atmosphere and even on the filter during sample collection. Diesel fuel contains polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and some alkyl derivatives. Both groups of compounds may survive the combustion process. PAHs are formed by the combustion of crankcase oil or may be resuspended from engine and/or exhaust deposits. The conversion of parent PAHs to oxygenated and nitrated PAHs in the combustion chamber or in the exhaust system is related to the vast amount of excess combustion air that is supplied to the engine and the high combustion temperature. Whether the occurrence of these derivatives is characteristic for the composition of diesel engine exhaust remains to be ascertained. After the emission of the particles, their properties may change because of atmospheric processes such as aging and resuspension. The particle-associated organics may also be subject to (photo)chemical conversions or the components may change during sampling and analysis. Measurement of emissions of incomplete combustion products as determined on a chassis dynamometer provides knowledge of the chemical composition of the particle-associated organics. This knowledge is useful as a basis for a toxicological evaluation of the health hazards of diesel engine emissions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbass MK, Williams PT, Andrews GE, Bartle KD (1987) The aging of lubricating oil, the influence of unburnt fuel and particulate SOF contamination. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 872085
Abbass MK, Andrews GE, Williams PT, Bartle KD, Davies IL, Tanui LK (1988) Diesel particulate emissions: pyrosynthesis of PAH from hexadecane. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 880345
Abdelnasser M, Hyland M, Jespersen ND (1986) Synthesis of mutagenic compounds in crankcase oils. Environ Sci Technol 20:145–149
Amann CA, Stivender DL, Plee SL, MacDonald JS (1980) Some rudiments of diesel particulate emissions. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 800251
Aoyagi Y, Kamimoto T, Matsui Y, Matsuoka S (1980) A gas sampling study on the formation processes of soot and NO in a DI diesel engine. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 800254
Barbella R, Bertoli C, Ciajolo A, D'Anna A (1988) Soot and unburnt liquid hydrocarbon emissions from diesel engines. Combust Sci Technol 59:183–198
Behymer TD, Hites RA (1985) Photolysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons adsorbed on simulated atmospheric particulates. Environ Sci Technol 19:1004–1006
Braddock JN, Perry Jr NK (1986) Gaseous and particulate emissions from gasoline- and diesel-powered heavy duty trucks. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 860617
Bradow RL (1982) Diesel particle and organic emissions: engine simulation, sampling, and artifacts. In: Lewtas J (ed) Carcinogenic and mutagenic effects of diesel engine exhaust. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, pp 33–50
Choudhury DR (1982) Characterization of polycyclic ketones and quinones in diesel emission particulates by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Environ Sci Technol 16:102–106
Clark CR, Henderson TR, Rover RE, Brooks AL, McClellan RO, Marschall WF, Naman TM (1982) Mutagenicity of diesel exhaust particle extracts: influence of fuel composition in two diesel engines. Fundam Appl Toxicol 2:38–43
CONCAWE (1987) Diesel fuel quality and its relationship with emissions from diesel engines. CONCAWE, The Hague
Cuthbertson RD, Shore PR, Sundström L, Heden PO (1987) Direct analysis of diesel particulate-bound hydrocarbons by gas chromatography with solid sample injection. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 870626
Dolan DF, Kittelson DB, Pui DYH (1980) Diesel exhaust particle size distribution measurement techniques. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 800187
Draper WM, Phillips J, Zeller HW (1988) Impact of a barium fuel additive on the mutagenicity and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon content of diesel exhaust particulate emissions. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 881651
Du C-J, Kittelson DB, Zweidinger RB (1984) Measurement of polycyclic aromatic compounds in the cylinder of an operating diesel engine. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no 840364
Egebäck KE, Bertilsson BM (1983) Chemical and biological characterization of exhaust emissions from vehicles fueled with gasoline, alcohol, LPG and diesel. National Swedish Protection Board, report no. snv pm 1635
Encyclopædia Brittanica (1984) The new Encyclopædia Brittanica, 15th edn. Encyclopædia Brittanica, Chicago
Grimmer G (1979) Sources and occurrence of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. In: Egan H (ed) Environmental carcinogens. Selected methods of analysis, vol 3. Analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in environmental samples. IARC Publ no 29. IARC, Lyon, pp 31–125
Grimmer G, Hildebrandt A (1975) Investigations on the carcinogenic burden by air pollution in man. XIII. Assessment of the contribution of passenger cars to air pollution by carcinogenic polycyclic hydrocarbons. Zentralbl Bakt Hyg 161:104–124
Groblicky PJ, Begeman CR (1979) Particle size variation in diesel exhaust. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 790421
Hampton CH, Pierson WR, Schuetzle D, Harvey TM (1983) Hydrocarbon gases emitted from vehicles on the road. 2. Determination of emission rates from diesel and spark-ignition vehicles. Environ Sci Technol 17:699–708
Hare CT (1986) The effects of diesel fuel properties on particulate emissions. In: Lee SD, Schneider T, Grant LD, Verkerk PJ (eds) Aerosols. Lewis, Chelsea, pp 501:514
Hare CT, Baines TM (1979) Characteristics of particulate and gaseous emissions from two diesel automobiles as functions of fuel and driving cycle. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 790424
Hare CT, Springer KJ, Bradow RL (1976) Fuel and additive effects on diesel particulate development and demonstration of methodology. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 760130
Hayano S, Jang-Ho L, Furuya K et al. (1985) Formation of hazardous substances and mutagenicity of PAH produced during the combustion process in a diesel engine. Atmos Environ 19:1009–1015
Henderson TR, Royer RE, Clark CR, Harvey TM, Hunt DF (1982) MS/MS analysis of diesel emissions and fuels treated with NO2. J Appl Toxicol 2:231–237
Henderson TR, Sun JD, Li AP et al. (1984) GC/MS and MS/MS studies of diesel exhaust mutagenicity and emissions from chemically defined fuels. Environ Sci Technol 18:428–434
Herr JD, Dukovich M, Lestz SS, Yergey JA, Risby TH, Tejada SB (1982) The role of nitrogen in the observed direct microbial mutagenic activity for diesel engine combustion in a single-cylinder DI engine. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no 820467
Hisamatsu Y, Nishimura T, Tanabe K, Matsushita H (1986) Mutagenicity of the photochemical reaction products of pyrene with nitrogen dioxide. Mutat Res 172:19–27
Huisingh J, Bradow R, Jungers R et al. (1987) Application of bioassay to the characterization of diesel particle emissions. In: Waters MD, Nesnow S, Huisingh JL, Sandhu SS, Claxton L (eds) Application of short-term bioassays in the fractionation and analysis of complex environmental mixtures. Plenum, New York, pp 382–418
IARC (1989) IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risk to humans. Diesel and gasoline engine exhausts and some nitroarenes. IARC, Lyon
Iida N, Suzuki Y, Sato GT, Sawada T (1986) Effects of intake oxygen concentration on the characteristics of particulate emissions from a D.I. diesel engine. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 861233
Israel GW, Zierock K-H, Mollerhauer K (1982) Größenverteilung und chemische Zusammensetzung der Partikelemissionen verschiedener Dieselmotoren. VDI-Berichte 429:279–286
Jensen TE, Hites RA (1983) Aromatic diesel emissions as a function of engine conditions. Anal Chem 55:594–599
Jensen TE, Richert JFO, Cleary AC, LaCouse DL, Gorse Jr RA (1986) 1-Nitropyrene in used diesel engine oil. J Am Pollut Control Assoc 26:1255–1256
Kamimoto T, Aoyagi Y, Matsui Y, Mastuoka S (1980) The effects of some engine variables on measured rates of air entrainment and heat release in a DI engine. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 800253
Lach G, Winckler J (1988) Specific problems of sampling and measuring diesel exhaust emissions. Society of Automotive Engineer paper no. 881763
Lehmann E, Rentel K-H, Allescher W, Homann R (1989) Gefährliche Arbeitsstoffe GA33: Messung der beruflichen Exposition gegenüber Dieselabgas. Bundesanstalt für Arbeitsschutz, Dortmund
Li AP, Royer RE, Brooks AL, McClellan RO (1982) Cytotoxicity of diesel exhaust particle extracts — a comparison among five diesel passenger cars of different manufacturers. Toxicology 24:1–8
Lies K-H (1989) Unregulated motor vehicle exhaust gas components. Volkswagen AG, Wolfsburg MacDonald JS, Plee SL, D'Arcy JB, Schreck RM (1980) Experimental measurements of the independent effects of dilution ratio and filter temperature on diesel exhaust particulate samples. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 800185
Manabe Y, Konouchi T, Wakisaka T, Tahra I, Ohnishi Y (1984) Mutagenic 1-nitropyrene in wastewater from oil-water separating tanks of gasoline stations and in used crankcase oil. Environ Mutagen 6:669–681
Mayer WJ, Lechman DC, Hilden DL (1980) The contribution of engine oil to diesel exhaust particulate emissions, Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 800256
Meyer JP, Grimmer G (1974) Einflüsse PAH-haltiger and PAH-freier Kraftstoffe auf die Emission von polycyclischen aromatischen Kohlenwasserstoffen eines Kraftfahrzeugs mit Ottomotor im Europa-test. DGMK-Forschungsbericht 4547, II, Hamburg
Moriske HJ, Rüden H (1988) Polare neutrale organische Verbindungen (POCN) im Stadtaerosol. Mitteilung: Vergleichende Untersuchungen von Emissions- und Immissionsstäuben in Berlin (West) Zentralbl Bakt Hyg 185:452–468
Murayama T, Miyamoto N, Chikahisa T, Yamane K (1986) Effects of combustion and injection systems on unburnt HC and particulate emissions from a DI diesel engine. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 861232
Nelson PF (1989) Combustion-generated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in diesel exhaust emissions. Fuel 68:283–286
Olah GA, Narang SC, Olah JA (1981) Nitration of naphthalene and remarks on the mechanism of electrophilic aromatic nitration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:3298–3300
Pipho MJ, Ambs JL, Kittelson DB (1986) In-cylinder measurements of particulate formation in an indirect injection diesel engine. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 860024
Plee SL, MacDonald JS (1980) Some mechanisms affecting the mass of diesel exhaust particulate collected following a dilution process. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 800186
Rosenkranz HS, Mermelstein R (1985) The genotoxicity, metabolism and carcinogenicity of nitrated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J Environ Sci Health 3:221–272
Ryan TW, Storment JO, Wright BR, Waytulonis R (1981) The effects of fuel properties and composition on diesel engine exhaust emissions — a review. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 810953
Saito T, Tolureo N, Katoh T (1982) Analysis of factors affecting the formation of major mutagenic substances in diesel particulate extracts. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 821244
Schuetzle D (1983) Sampling of vehicle emissions for chemical analysis and biological testing. Environ Health Perspect 47:65–80
Schuetzle D, Frazier JA (1986) Factors influencing the emission of vapor and particulate phase components from diesel engines. In: Ishinishi N, Koizumi A, McClellan RO, Stöber W (eds) Carcinogenic and mutagenic effects of diesel engine exhaust. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, pp 41–63
Schuetzle D, Skewes LM, Fisher GE, Levine SP, Gorse Jr RA (1981) Determination of sulfates in diesel particulates. Anal Chem 53:837–840
Serageldin MA (1981) Soot formation in small flames. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 811197
Stärk G, Stauff J, Miltenburger HG, Stumm-Fischer I (1985) Photodecomposition of 1-nitropyrene and other direct-acting mutagens extracted from diesel exhaust particulates. Mutat Res 155:27–33
Steenlage R, Rijkeboer RC (1985) Oriënterende metingen van de emissie van schadelijke en hinderlijke organische verbindingen afkomstig van gemotoriseerd wegverkeer. TNO, Delft, Report no. G 1115
Stenberg U, Alsberg T, Westerholm W (1983) Emission of carcinogenic components with automobile exhausts. Environ Health Perspect 47:53–56
Truex TJ, Pierson WR, McKee DE (1980) Sulfate in diesel exhaust. J Environ Sci Technol 14:1118–1121
Uyehara OA (1980) Effect of burning zone A/F, fuel H/C on soot formation and thermal efficiency. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 800093
Van Beckhoven LC (1991) Effects of fuel properties on diesel engine emissions — a review of information available to EEC-MVEG group. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 910608
Wade WR (1980) Light-duty diesel NOx-HC-particulate trade-off studies. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 800335
Wade WR, Jones CM (1984) Current and future light duty diesel engines and their fuels. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 840105
Weidmann K, Menrad H, Reders K, Hutcheson RC (1988) Diesel fuel quality effects on exhaust emissions. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 881649
Westerholm R, Alsber T, Strandell M et al. (1986) Chemical analysis and biological testing of emissions from a heavy duty diesel truck with and without two different particulate traps. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 860014
Williams PT, Bartle KD, Andrews GE (1986a) The relation between polycyclic aromatic compounds in diesel fuel and exhaust particulates. Fuel 65:1150–1158
Williams R, Sparacino C, Petersen B, Bumgarner J, Jungers RH, Lewtas J (1986b) Comparative characterization of organic emissions from diesel particles, coke oven mains, roofing tar vapors and cigarette smoke condensate. Int J Environ Anal Chem 26:27–49
Williams PT, Andrews GE, Bartle KD (1987) The role of lubricating oil in diesel particulate and particulate PAH emissions. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 872084
Williams PT, Abbass MK, Tam LP, Andrews GE, Ng KL, Bartle KD (1988) A comparison of exhaust pipe, dilution tunnel and road side diesel particulate SOF and gaseous hydrocarbon emissions, Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 880351
Yamaki N, Kohno T, Ishiwata S (1986) The state of the art on the chemical characterization of diesel particulates in Japan. In: Ishinishi N, Koizumi A, McClellan RO, Stöber W (eds) Carcinogenic and mutagenic effects of diesel engine exhaust. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, pp 17–40
Yoshida E, Nomura H, Sekimoto N (1986) Fuel and engine effects on diesel exhaust emissions. Society of Automotive Engineers paper no. 860619
Zweidinger RB (1982) Emission factors from diesel and gasoline powered vehicles: correlation with the Ames test. In: Lewtas J (ed) Toxicological effects of emissions from diesel engines. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, pp 83–96
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scheepers, P.T.J., Bos, R.P. Combustion of diesel fuel from a toxicological perspective. Int. Arch Occup Environ Heath 64, 149–161 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00380904
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00380904