Abstract
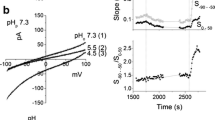
In primary cultures of rat osteoblasts, studied with the whole-cell configuration of the patch-clamp technique, 8-bromo-cyclic AMP (8BrcAMP) forskolin (FS) and 1–34 parathyroid hormone (PTH) were shown to activate a Cl conductance. This conductance shows a pronounced outward rectification, even with symmetrical Cl concentrations. It is blocked partially and reversibly by 4,4′-diisothiocyanatostilbene 2,2′-disulfonic acid (DIDS) or diphenylcarboxylate (DPC). The blockade induced by DIDS is time-and voltage-dependent. The Cl responses to FS and PTH develop slowly, after a delay of several seconds and are very slowly reversible. These responses were observed only in a fraction of the cells tested and their detection was favoured by cell dialysis. This Cl current should be taken into account for studying possible modulations of the voltage-gated Ca currents of osteoblasts. It is suggested that its physiological role may be related to the well-known morphological changes induced by PTH in osteoblasts. The cyclic AMP-sensitivity, the outward rectification and the sensitivity to dialysis of this Cl current are reminiscent of the properties of the cystic fibrosis-sensitive Cl channels of epithelial cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bean BP (1989) Classes of calcium channel in vertebrate cells. Annu Rev Physiol 51:367–384
Chesnoy-Marchais D, Fritsch J (1988) Voltage-gated sodium and calcium currents in rat osteoblasts. J Physiol (Lond) 398:291–311
Edelman A, Fritsch J, Balsan S (1986) Short-term effects of PTH on cultured rat osteoblasts: changes in membrane potential. Am J Physiol 251:C483–490
Frizzell RA, Rechkemmer GR, Schoemaker RL (1986) Altered regulation of airway epithelial cell chloride channels in cystic fibrosis. Science 233:558–560
Gray PTA, Ritchie JM (1986) A voltage-gated chloride conductance in rat cultured astrocytes. Proc R Soc Lond B 228:267–288
Greger R, Schlatter E, Gögelein H (1985) Cl-channels in the apical cell membrane of the rectal gland “induced” by cAMP. Pflügers Arch 403:446–448
Greger R, Schlatter E, Gögelein H (1987) Chloride channels in the luminal membrane of the rectal gland of the dogfish (Squalus acanthias). Properties of the ‘larger” conductance channel. Pflügers Arch 409:114–121
Halm DR, Rechkemmer GR, Schoumacher RA, Frizzell RA (1988) Apical membrane chloride channels in a colonic cell line activated by secretory agonists. Am J Physiol 254:C505–511
Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ (1981) Improved patch-clamp technique for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflügers Arch 391:85–100
Hayslett JP, Gögelein H, Kunzelmann K, Greger R (1987) Characteristics of apical chloride channels in human colon cells (HT 29). Pflügers Arch 410:487–494
Hymel L, Striessnig J, Glossmann H, Schindler H (1988) Purified skeletal muscle 1,4-dihydropyridine receptor forms phosphorylation-dependent oligomeric calcium channels in planar bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:4290–4294
Johnson JW, Ascher P (1987) Glycine potentiates the NMDA response in cultured mouse brain neurons. Nature 325:529–531
Li M, McCann JD, Liedtke CM, Nairn AC, Greengard P, Welsh MJ (1988) Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase opens chloride channels in normal but not cystic fibrosis airway epithelium. Nature 331:358–360
Lieberherr M (1987) Effects of vitamin D3 metabolites on cytosolic free calcium in confluent mouse osteoblasts. J Biol Chem 262:13168–13173
Lindskog S, Blomlöf L, Hammarström L (1987) Comparative effects of parathyroid hormone on osteoblasts and cementoblasts. J Clin Periodontol 14:386–389
Löwik CWGM, Van Leeuwen JPTM, Van der Meer J, Van Zeeland JK, Scheven BAA, Hermann-Erlee MPM (1985) A two-receptor model for the action of parathyroid hormone on osteoblast: a role for intracellular calcium and cAMP. Cell Calcium 6:311–326
Ma J, Coronado R (1988) Heterogeneity of conductance states in calcium channels of skeletal muscle. Biophys J 53:387–395
Palade PT, Barchi RL (1977) On the inhibition of muscle membrane chloride conductance by aromatic carboxylic acids. J Gen Physiol 69:879–896
Penner R, Matthews G, Neher E (1988) Regulation of calcium influx by second messengers in rat mast cells. Nature 334:499–504
Reid IR, Civitelli R, Halstead LR, Avioli LV, Hruska KA (1987) Parahyroid hormone acutely elevates intracellular calcium in osteoblast like cells. Am J Physiol 252:E45-E51
Rodan GA, Rodan SB (1984) Expression of the osteoblastic phenotype. In: Peck WA (ed) Bone and mineral research, Annual 2. Elsevier, Amsterdam New York, pp 244–285
Schoumacher RA, Shoemaker RL, Halm DR, Tallant EA, Wallace RW, Frizzell RA (1987) Phosphorylation fails to activate chloride channels from cystic fibrosis airway cells. Nature 330:752–754
Ship S, Shami Y, Breuer W, Rothstein A (1977) Synthesis of tritiated 4,4′-diisothiocyano — 2,2′-stilbene disulfonic acid (3([H] DIDS) and its covalent reaction with sites related to anion transport in red blood cells. J Membr Biol 33:311–324
Seamon KB, Padget W, Daly JW (1981) Forskolin: unique diterpene activator of adenylate cyclase in membranes and in intact cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:3363–3367
Van Leeuwen JPTM, Bos MP, Löwik CWGM, Hermann-Erlee MPM (1988) Effect of parathyroid hormone and parathyroid hormone fragments on the intracellular ionized calcium concentration in an osteoblast cell line. Bone and Mineral 4:177–188
Wangemann P, Wittner M, Di Stefano A, Englert HC, Lang HJ, Schlatter E, Greger R (1986) Cl−-channel blockers in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle. Structure activity relationship. Pflügers Arch 407 (Suppl 2):S128-S141
Welsh MJ (1986) Single apical membrane anion channels in primary cultures of canine tracheal epithelium. Pflügers Arch 407 (Suppl 2): S116-S122
Welsh MJ, Liedtke CM (1986) Chloride and potassium channels in cystic fibrosis airway epithelia. Nature 322:467–470
Yamaguchi DT, Hahn TJ, Iida-Klein A, Kleeman CR, Muallem S (1987) Parathyroid hormone-activated calcium channels in an osteoblast-like clonal oesteosarcoma cell line. J Biol Chem 262:7711–7718
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chesnoy-Marchais, D., Fritsch, J. Chloride current activated by cyclic AMP and parathyroid hormone in rat osteoblasts. Pflugers Arch. 415, 104–114 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00373147
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00373147