Abstract
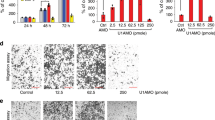
Alterations in cathepsin L expression and trafficking have been associated with the progression and metastasis of several tumor entities. In the present study, we examined the effects of various cathepsin L antisense (as) phosphorothioate oligonucleotides on both the expression of cathepsin L and the invasive potential of the human osteosarcoma cell line MNNG/HOS. Seven oligonucleotides of 20-bp length each and one random control oligonucleotide were chosen to block cathepsin L expression. Northern blot analysis demonstrated a significant reduction in cathepsin L mRNA expression by the six antisense oligonucleotides at a concentration of 10 μM. Cathepsin L protein expression was reduced significantly (50–85%) by the antisense oligonucleotides, as compared with the controls. Adhesion to matrices of collagen I and matrigel was not affected. In in vitro motility and invasion assays performed in uncoated and precoated transwell chambers, the ability of cells to migrate through the filters was inhibited by 35–75% using antisense oligonucleotides. The random control did not show any inhibitory effect. These data demonstrate that in MNNG/HOS cells cathepsin L influences cellular malignancy by promoting migration and basement membrane degradation. Cancer Gene Therapy (2001) 8, 522–528
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mignatti P, Rifkin DB . Biology and biochemistry of proteinases in tumor invasion Physiol Rev 1993 73: 161–195
Sloane BF, Rozhin J, Krepela E, Ziegler G, Sameni M . The malignant phenotype and cysteine proteinases Biomed Biochim Acta 1991 50: 549–554
Berquin IM, Sloane BF . Cysteinprotease and tumor progression Perspect Drug Discovery Des 1994 2: 371–388
Lah TT, Kos J . Cysteine proteinases in cancer Progression and their clinical relevance for prognosis Biol Chem 1998 379: 125–130
Koblinski JE, Ahram M, Sloane BF . Unraveling the role of proteases in cancer Clin Chim Acta 2000 291: 113–135
Barrett AJ, Kirschke H. Cathepsin B, Cathepsin H, Cathepsin L . Methods Enzymol 1981 80: 535–561
Chauhan SS, Goldstein LJ, Gottesman MM . Expression of cathepsin L in human tumors Cancer Res 1991 51: 1478–1481
Kos J, Stabuc B, Schweiger A, et al . Cathepsin b, H, and L and their inhibitors stefin A and cystatin C in sera of melanoma patients Clin Cancer Res 1997 3: 1815–1822
Krepela E, Prochazka J, Karova B, Cermak J, Roubkova H . Cysteine proteases and cysteine protease inhibitors in non–small cell lung cancer Neoplasma 1998 45: 318–331
Foekens JA, Kos J, Peters HA, et al . Prognostic significance of cathepsin B and L in primary human breast cancer J Clin Oncol 1998 16: 1013–1021
Friedrich B, Jung K, Lein M, et al . Cathepsin B, H, L and cysteine protease inhibitors in malignant prostate cell lines, primary cultured prostatic cells and prostatic tissue Eur J Cancer 1999 35: 138–144
Thomssen C, Oppelt P, Janicke F, et al . Identification of low-risk node-negative breast cancer patients by tumor biological factors PAI-1 and cathepsin L Anticancer Res 1998 18: 2173–2180
Weber E, Günther D, Laube F, Wiederanders B, Kirschke H . Hybridoma cells producing antibodies to cathepin L have greatly reduced potential for tumour growth J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 1994 120: 564–567
Navab R, Mort JS, Brodt P . Inhibition of carcinoma cell invasion and liver metastases formation by the cysteine proteinase inhibitor E-64 Clin Exp Metastasis 1997 15: 121–129
Sexton PS, Cox JL . Inhibition of motility and invasion of B16 melanoma by the overexpression of cystatin C Melanoma Res 1997 7: 97–101
Kolkhorst V, Stürzebecher J, Wiederanders B . Inhibition of tumour cell invasion by protease inhibitors: correlation with protease profile J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 1998 124: 598–606
Hélène C, Toulmé JJ . Specific regulation of gene expression by antisense, sense and antigen nucleic acids Biochim Biophys Acta 1990 1049: 99–125
Kirschke H, Clausen T, Göhring B, et al . Concentration of lysosomal cysteine proteases are decreased in renal cell carcinoma compared with normal kidney J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 1997 123: 402–406
Ledakis P, Tester WT, Rosenberg N, Romero-Fischmann D, Daskal I, Lah TT . Cathepsin D, B, and L in malignant human lung tissue Clin Cancer Res 1996 2: 561–568
Lah TT, Calaf G, Kalman E, et al . Cathepsin D, B and L in breast carcinoma and in transformed human breast epithelial cells (HBEC) Biol Chem 1995 376: 357–363
Castiglioni T, Merino MJ, Elsner B, Lah TT, Sloane BF, Emmert-Buck MR . Immunohistochemical analysis of cathepsin D, B, and L in human breast cancer Hum Pathol 1994 25: 857–862
Plebani M, Herszenyi L, Cardin R, et al . Cysteine and serine proteases in gastric cancer Cancer 1995 76: 367–375
Sivaparvathi M, Yamamoto M, Nicolson GL, et al . Expression of cysteine protease inhibitors in human gliomas and meningiomas Clin Exp Metastasis 1996 14: 27–34
Park IC, Lee SY, Jeon DG, et al . Enhanced expression of cathepsin L in metastatic bone tumors J Korean Med Sci 1996 11: 144–148
Colman A . Antisense strategies in cell and developmental biology J Cell Sci 1990 97: 399–409
Wagner RW . Gene inhibition using antisense oligodeoxynucleotides Nature 1994 372: 333–335
Boiziau C, Kurfurst R, Cazenave C, et al . Inhibition of translation initiation by antisense oligonucleotides via an Rnase H independent mechanism Nucleic Acids Res 1991 19: 1113–1119
Dean NM, McKay R . Inhibition of protein kinase C-alpha expression in mice after systemic administration of phosphorothioate antisense oligodeoxynucleotides Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994 91: 11762–11770
Crooke ST, Lemonidis KM, Neilson L, Griffey R, Lesnik EA, Monia BP . Kinetic characteristics of Escherichia coli RNase H1: cleavage of various antisense oligonucleotide–RNA duplexes Biochem J 1995 312: 599–608
Kirschke H, Eerola R, Hopsu-Havu VK, Brömme D, Vuorio E . Antisense RNA inhibition of cathepsin L expression reduces tumorigenicity of malignant cells Eur J Cancer 2000 36: 787–795
Krueger S, Haeckel C, Buehling F, Roessner A . Inhibitory effects of antisense cathepsin B cDNA transfection on invasion and motility in a human osteosarcoma cell line Cancer Res 1999 59: 6010–6014
Haeckel C, Krueger S, Roessner A . Antisense inhibition of urokinase: effect on malignancy in a human osteosarcoma cell line Int J Cancer 1998 77: 153–160
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB387). We gratefully acknowledge the excellent technical assistance of Doreen Gärtner. The authors thank Bernd Wüsthoff for help in preparing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krueger, S., Kellner, U., Buehling, F. et al. Cathepsin L antisense oligonucleotides in a human osteosarcoma cell line: Effects on the invasive phenotype. Cancer Gene Ther 8, 522–528 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700341
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700341
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
CDH4 is a novel determinant of osteosarcoma tumorigenesis and metastasis
Oncogene (2018)
-
Cathepsin L in Normal and Pathological Bone Remodeling
Clinical Reviews in Bone and Mineral Metabolism (2011)
-
Cathepsin L increased level upon Ras mutants expression: the role of p38 and p44/42 MAPK signaling pathways
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2010)
-
Frequent loss of cystatin E/M expression implicated in the progression of prostate cancer
Oncogene (2009)
-
Loss of responsiveness to IGF-I in cells with reduced cathepsin L expression levels
Oncogene (2008)