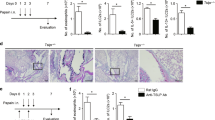
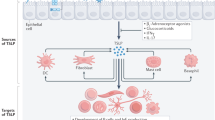
Abstract
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) is an interleukin 7 (IL-7)-like cytokine originally characterized by its ability to promote the activation of B cells and dendritic cells (DCs). Subsequent studies have shown that TSLP promotes T helper type 2 (TH2) cell responses associated with immunity to some helminth parasites and the pathogenesis of many inflammatory diseases, including atopic dermatitis and asthma. This review will focus on recent findings indicating that in addition to influencing B cell and DC function, TSLP can promote TH2 cytokine–associated inflammation by directly promoting the effector functions of CD4+ TH2 cells, basophils and other granulocyte populations while simultaneously limiting the expression of DC-derived proinflammatory cytokines and promoting regulatory T cell responses in peripheral tissues.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Friend, S.L. et al. A thymic stromal cell line supports in vitro development of surface IgM+ B cells and produces a novel growth factor affecting B and T lineage cells. Exp. Hematol. 22, 321–328 (1994).
Sims, J.E. et al. Molecular cloning and biological characterization of a novel murine lymphoid growth factor. J. Exp. Med. 192, 671–680 (2000).
Ray, R.J., Furlonger, C., Williams, D.E. & Paige, C.J. Characterization of thymic stromal-derived lymphopoietin (TSLP) in murine B cell development in vitro. Eur. J. Immunol. 26, 10–16 (1996).
Reche, P.A. et al. Human thymic stromal lymphopoietin preferentially stimulates myeloid cells. J. Immunol. 167, 336–343 (2001).
Quentmeier, H. et al. Cloning of human thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) and signaling mechanisms leading to proliferation. Leukemia 15, 1286–1292 (2001).
Park, L.S. et al. Cloning of the murine thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) receptor: Formation of a functional heteromeric complex requires interleukin 7 receptor. J. Exp. Med. 192, 659–670 (2000).
Pandey, A. et al. Cloning of a receptor subunit required for signaling by thymic stromal lymphopoietin. Nat. Immunol. 1, 59–64 (2000).
Levin, S.D. et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin: a cytokine that promotes the development of IgM+ B cells in vitro and signals via a novel mechanism. J. Immunol. 162, 677–683 (1999).
Isaksen, D.E. et al. Requirement for STAT5 in thymic stromal lymphopoietin-mediated signal transduction. J. Immunol. 163, 5971–5977 (1999).
Al Shami, A. et al. A role for thymic stromal lymphopoietin in CD4+ T cell development. J. Exp. Med. 200, 159–168 (2004).
Soumelis, V. et al. Human epithelial cells trigger dendritic cell mediated allergic inflammation by producing TSLP. Nat. Immunol. 3, 673–680 (2002).
Zhou, B. et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) as a key initiator of allergic airway inflammation in mice. Nat. Immunol. 6, 1047–1053 (2005).
Watanabe, N. et al. Human thymic stromal lymphopoietin promotes dendritic cell–mediated CD4+ T cell homeostatic expansion. Nat. Immunol. 5, 426–434 (2004).
Ito, T. et al. TSLP-activated dendritic cells induce an inflammatory T helper type 2 cell response through OX40 ligand. J. Exp. Med. 202, 1213–1223 (2005).
Wang, Y.H. et al. Maintenance and polarization of human TH2 central memory T cells by thymic stromal lymphopoietin-activated dendritic cells. Immunity 24, 827–838 (2006).
Rimoldi, M. et al. Intestinal immune homeostasis is regulated by the crosstalk between epithelial cells and dendritic cells. Nat. Immunol. 6, 507–514 (2005).
Rimoldi, M. et al. Monocyte-derived dendritic cells activated by bacteria or by bacteria-stimulated epithelial cells are functionally different. Blood 106, 2818–2826 (2005).
Zaph, C. et al. Epithelial-cell-intrinsic IKK-β expression regulates intestinal immune homeostasis. Nature 446, 552–556 (2007).
Taylor, B.C. et al. TSLP regulates intestinal immunity and inflammation in mouse models of helminth infection and colitis. J. Exp. Med. 206, 655–667 (2009).
Lambrecht, B.N. et al. Myeloid dendritic cells induce Th2 responses to inhaled antigen, leading to eosinophilic airway inflammation. J. Clin. Invest. 106, 551–559 (2000).
Lambrecht, B.N. & Hammad, H. Biology of lung dendritic cells at the origin of asthma. Immunity 31, 412–424 (2009).
van Rijt, L.S. et al. In vivo depletion of lung CD11c+ dendritic cells during allergen challenge abrogates the characteristic features of asthma. J. Exp. Med. 201, 981–991 (2005).
Pearce, E.J., Kane, C.M. & Sun, J. Regulation of dendritic cell function by pathogen-derived molecules plays a key role in dictating the outcome of the adaptive immune response. Chem. Immunol. Allergy 90, 82–90 (2006).
Perrigoue, J.G. et al. MHC class II–dependent basophil-CD4+ T cell interactions promote TH2 cytokine–dependent immunity. Nat. Immunol. 10, 697–705 (2009).
Sokol, C.L. et al. Basophils function as antigen-presenting cells for an allergen-induced T helper type 2 response. Nat. Immunol. 10, 713–720 (2009).
Yoshimoto, T. et al. Basophils contribute to TH2-IgE responses in vivo via IL-4 production and presentation of peptide–MHC class II complexes to CD4+ T cells. Nat. Immunol. 10, 706–712 (2009).
Massacand, J.C. et al. Helminth products bypass the need for TSLP in Th2 immune responses by directly modulating dendritic cell function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 13968–13973 (2009).
Omori, M. & Ziegler, S. Induction of IL-4 expression in CD4+ T cells by thymic stromal lymphopoietin. J. Immunol. 178, 1396–1404 (2007).
Allakhverdi, Z., Comeau, M.R., Jessup, H.K. & Delespesse, G. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin as a mediator of crosstalk between bronchial smooth muscles and mast cells. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 123, 958–960 (2009).
Allakhverdi, Z. et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin is released by human epithelial cells in response to microbes, trauma, or inflammation and potently activates mast cells. J. Exp. Med. 204, 253–258 (2007).
Nagata, Y., Kamijuku, H., Taniguchi, M., Ziegler, S. & Seino, K. Differential role of thymic stromal lymphopoietin in the induction of airway hyperreactivity and Th2 immune response in antigen-induced asthma with respect to natural killer T cell function. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 144, 305–314 (2007).
Wong, C.K., Hu, S., Cheung, P.F. & Lam, C.W. TSLP induces chemotactic and pro-survival effects in eosinophils: implications in allergic inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. published online, doi:10.1165/rcmb.2009-0168OC (20 October 2009).
Iliev, I.D., Matteoli, G. & Rescigno, M. The yin and yang of intestinal epithelial cells in controlling dendritic cell function. J. Exp. Med. 204, 2253–2257 (2007).
Iliev, I.D. et al. Human intestinal epithelial cells promote the differentiation of tolerogenic dendritic cells. Gut 58, 1481–1489 (2009).
Iwasaki, A. Mucosal dendritic cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 25, 381–418 (2007).
Coombes, J.L. & Powrie, F. Dendritic cells in intestinal immune regulation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 8, 435–446 (2008).
Sun, C.M. et al. Small intestine lamina propria dendritic cells promote de novo generation of Foxp3 Treg cells via retinoic acid. J. Exp. Med. 204, 1775–1785 (2007).
Coombes, J.L. et al. A functionally specialized population of mucosal CD103+ DCs induces Foxp3+ regulatory T cells via a TGF-β and retinoic acid-dependent mechanism. J. Exp. Med. 204, 1757–1764 (2007).
Iwasaki, A. & Kelsall, B.L. Freshly isolated Peyer's patch, but not spleen, dendritic cells produce interleukin 10 and induce the differentiation of T helper type 2 cells. J. Exp. Med. 190, 229–239 (1999).
Rimoldi, M. et al. Intestinal immune homeostasis is regulated by the corsstalk between epithelial cells and dendritic cells. Nat. Immunol. 6, 507–514 (2005).
Zeuthen, L.H., Fink, L.N. & Frokiaer, H. Epithelial cells prime the immune response to an array of gut-derived commensals towards a tolerogenic phenotype through distinct actions of thymic stromal lymphopoietin and transforming growth factor-beta. Immunology 123, 197–208 (2008).
Ramalingam, T.R. et al. Regulation of helminth-induced Th2 responses by thymic stromal lymphopoietin. J. Immunol. 182, 6452–6459 (2009).
Ker, J. & Hartert, T.V. The atopic march: what's the evidence? Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 103, 282–289 (2009).
Hahn, E.L. & Bacharier, L.B. The atopic march: the pattern of allergic disease development in childhood. Immunol. Allergy Clin. North Am. 25, 231–246 (2005).
Spergel, J.M. & Paller, A.S. Atopic dermatitis and the atopic march. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 112, S118–S127 (2003).
Ying, S. et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin expression is increased in asthmatic airways and correlates with expression of Th2-attracting chemokines and disease severity. J. Immunol. 174, 8183–8190 (2005).
Miyata, M. et al. Mast cell regulation of epithelial TSLP expression plays an important role in the development of allergic rhinitis. Eur. J. Immunol. 38, 1487–1492 (2008).
Mou, Z. et al. Overexpression of thymic stromal lymphopoietin in allergic rhinitis. Acta Otolaryngol. (Stockh.) 8, 1–5 (2008).
Gudbjartsson, D.F. et al. Sequence variants affecting eosinophil numbers associate with asthma and myocardial infarction. Nat. Genet. 41, 342–347 (2009).
He, H.Q. et al. A thymic stromal lymphopoietin gene variant is associated with asthma and airway hyperresponsiveness. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 124, 222–229 (2009).
Hunninghake, G.M. et al. Sex-stratified linkage analysis identifies a female-specific locus for IgE to cockroach in Costa Ricans. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 177, 830–836 (2008).
Harada, M. et al. Functional analysis of the thymic stromal lymphopoietin variants in human bronchial epithelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 40, 368–374 (2009).
Yoo, J. et al. Spontaneous atopic dermatitis in mice expressing an inducible thymic stromal lymphopoietin transgene specifically in the skin. J. Exp. Med. 202, 541–549 (2005).
Li, M. et al. Retinoid X receptor ablation in adult mouse keratinocytes generates an atopic dermatitis triggered by thymic stromal lymphopoietin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 14795–14800 (2005).
Demehri, S. et al. Notch-deficient skin induces a lethal systemic B-lymphoproliferative disorder by secreting TSLP, a sentinel for epidermal integrity. PLoS Biol. 6, e123 (2008).
Judge, M.R., Morgan, G. & Harper, J.I. A clinical and immunological study of Netherton's syndrome. Br. J. Dermatol. 131, 615–621 (1994).
Chavanas, S. et al. Mutations in SPINK5, encoding a serine protease inhibitor, cause Netherton syndrome. Nat. Genet. 25, 141–142 (2000).
Demehri, S., Morimoto, M., Holtzman, M.J. & Kopan, R. Skin-derived TSLP triggers progression from epidermal-barrier defects to asthma. PLoS Biol. 7, e1000067 (2009).
Zhang, Z. et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin overproduced by keratinocytes in mouse skin aggravates experimental asthma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 1536–1541 (2009).
Headley, M.B. et al. TSLP conditions the lung immune environment for the generation of pathogenic innate and antigen-specific adaptive immune responses. J. Immunol. 182, 1641–1647 (2009).
Ying, S. et al. Expression and cellular provenance of thymic stromal lymphopoietin and chemokines in patients with severe asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Immunol. 181, 2790–2798 (2008).
Al Shami, A., Spolski, R., Kelly, J., Keane-Myers, A. & Leonard, W.J. A role for TSLP in the development of inflammation in an asthma model. J. Exp. Med. 202, 829–839 (2005).
Lee, H.C. & Ziegler, S.F. Inducible expression of the proallergic cytokine thymic stromal lymphopoietin in airway epithelial cells is controlled by NFκB. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 914–919 (2007).
Kato, A., Favoreto, S. Jr, Avila, P.C. & Schleimer, R.P. TLR3- and Th2 cytokine-dependent production of thymic stromal lymphopoietin in human airway epithelial cells. J. Immunol. 179, 1080–1087 (2007).
Holt, P.G. & Sly, P.D. Interactions between RSV infection, asthma, and atopy: unraveling the complexities. J. Exp. Med. 196, 1271–1275 (2002).
Hall, C.B. Respiratory syncytial virus and parainfluenza virus. N. Engl. J. Med. 344, 1917–1928 (2001).
Martinez, F.D. Respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolotis and the pathogenesis of childhood asthma. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 22, S76–S82 (2003).
Stein, R.T. et al. Respiratory syncytial virus in early life and risk of wheeze and allergy by age 13 years. Lancet 354, 541–545 (1999).
Yoon, J.S., Kim, H.H., Lee, Y. & Lee, J.S. Cytokine induction by respiratory syncytial virus and adenovirus in bronchial epethelial cells. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 42, 277–282 (2007).
Leonard, W.J. TSLP: finally in the limelight. Nat. Immunol. 3, 605–607 (2002).
Kido, M. et al. Helicobacter pylori promotes the production of thymic stromal lymphopoietin by gastric epithelial cells and induces dendritic cell-mediated inflammatory Th2 responses. Infect. Immun. 78, 108–114 (2010).
Acknowledgements
We thank D. Campbell, M. Siracusa and G. Sonnenberg for reviewing the manuscript. Supported by the National Institutes of Health (AI068731, AI044259, AR055695 and AR56113 to S.F.Z., and AI061570, AI074878 and AI083480 to D.A.), the Burroughs Wellcome Fund (D.A.), the Crohn's and Colitis Foundation of America (D.A.) and the University of Pennsylvania (D.A.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ziegler, S., Artis, D. Sensing the outside world: TSLP regulates barrier immunity. Nat Immunol 11, 289–293 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.1852
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.1852
This article is cited by
-
Pathogenesis of allergic diseases and implications for therapeutic interventions
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2023)
-
Assessment of TSLP, IL 25 and IL 33 in patients with shrimp allergy
Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology (2021)
-
Blood tryptase and thymic stromal lymphopoietin levels predict the risk of exacerbation in severe asthma
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
CASCADE: a phase 2, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial to evaluate the effect of tezepelumab on airway inflammation in patients with uncontrolled asthma
Respiratory Research (2020)
-
Knockdown of sodium channel Nax reduces dermatitis symptoms in rabbit skin
Laboratory Investigation (2020)