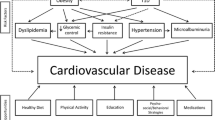
Abstract
In the United States, cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of mortality in adults with diabetes over age 30 years. Studies in persons without diabetes have shown that atherosclerosis, a central factor in cardiovascular disease, begins in childhood and the presence of cardiovascular disease risk factors in youth lead to increased cardiovascular disease risk in adults. Therefore, youth with diabetes are at increased risk for developing cardiovascular disease as adults and there is a role for risk factor screening and addressing modifiable factors to lower cardiovascular disease risk starting in childhood. This paper reviews the literature on traditional cardiovascular disease risk factors in youth with diabetes including hyperglycemia, hypertension, dyslipidemia, smoking, obesity and family history of cardiovascular disease with an emphasis on type 1 diabetes as well as current American Diabetes Association guidelines for screening and treatment of modifiable risk factors. Current roles of inflammatory markers and measures of subclinical vascular changes such as arterial stiffness are also discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moss SE, Klein R, Klein BE. Cause-specific mortality in a population-based study of diabetes. Am J Public Health 1991;81:1158–62.
Laing SP, Swerdlow AJ, Slater SD, Botha JL, Burden AC, Waugh NR, et al. The British diabetic association cohort study. II. Cause-specific mortality in patients with insulin-treated diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med 1999;16:466–71.
Stamler J, Vaccaro O, Neaton JD, Wentworth D. Diabetes, other risk factors, and 12-yr cardiovascular mortality for men screened in the multiple risk factor intervention trial. Diabetes Care 1993;16:434–44.
Orchard TJ, Olson JC, Erbey JR, Williams K, Forrest KY, Smithline KL, et al. Insulin resistance-related factors, but not glycemia, predict coronary artery disease in type 1 diabetes: 10-year follow-up data from the Pittsburgh Epidemiology of Diabetes Complications Study. Diabetes Care 2003;26:1374–9.
Soedamah-Muthu SS, Chaturvedi N, Toeller M, Ferriss B, Reboldi P, Michel G, et al. Risk factors for coronary heart disease in type 1 diabetic patients in Europe: the EURODIAB Prospective Complications Study. Diabetes Care 2004;27:530–7.
Krolewski AS, Kosinski EJ, Warram JH, Leland OS, Busick EJ, Asmal AC, et al. Magnitude and determinants of coronary artery disease in juvenile-onset, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Am J Cardiol 1987;59:750–5.
Pambianco G, Costacou T, Ellis D, Becker DJ, Klein R, Orchard TJ. The 30-year natural history of type 1 diabetes complications: the Pittsburgh epidemiology of diabetes complications study experience. Diabetes 2006;55:1463–9.
Strong JP, Malcom GT, McMahan CA, Tracy RE, Newman III WP, Herderick EE, et al. Prevalence and extent of atherosclerosis in adolescents and young adults: implications for prevention from the pathobiological determinants of atherosclerosis in youth study. JAMA 1999;281:727–35.
Berenson GS, Wattigney WA, Tracy RE, Newman WP III, Srinivasan SR, Webber LS, et al. Atherosclerosis of the aorta and coronary arteries and cardiovascular risk factors in persons aged 6 to 30 years and studied at necropsy (The Bogalusa Heart Study). Am J Cardiol 1992;70:851–8.
Davis PH, Dawson JD, Riley WA, Lauer RM. Carotid intimal-medial thickness is related to cardiovascular risk factors measured from childhood through middle age: the muscatine study. Circulation 2001;104:2815–9.
Li S, Chen W, Srinivasan SR, Bond MG, Tang R, Urbina EM, et al. Childhood cardiovascular risk factors and carotid vascular changes in adulthood: the Bogalusa Heart Study. JAMA 2003;290:2271–6.
Raitakari OT, Juonala M, Kahonen M, Taittonen L, Laitinen T, Maki-Torkko N, et al. Cardiovascular risk factors in childhood and carotid artery intima-media thickness in adulthood: the cardiovascular risk in young finns study. JAMA 2003;290:2277–83.
Crall FV Jr., Roberts WC. The extramural and intramural coronary arteries in juvenile diabetes mellitus: analysis of nine necropsy patients aged 19 to 38 years with onset of diabetes before age 15 years. Am J Med 1978;64:221–30.
Valsania P, Zarich SW, Kowalchuk GJ, Kosinski E, Warram JH, Krolewski AS. Severity of coronary artery disease in young patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Am Heart J 1991;122:695–700.
Chun BY, Dobson AJ, Heller RF. The impact of diabetes on survival among patients with first myocardial infarction. Diabetes Care 1997;20:704–8.
Miettinen H, Lehto S, Salomaa V, Mahonen M, Niemela M, Haffner SM, et al. Impact of diabetes on mortality after the first myocardial infarction. The FINMONICA myocardial infarction register study group (see comments). Diabetes Care 1998;21:69–75.
Savage MP, Krolewski AS, Kenien GG, Lebeis MP, Christlieb AR, Lewis SM. Acute myocardial infarction in diabetes mellitus and significance of congestive heart failure as a prognostic factor. Am J Cardiol 1988;62:665–9.
Ferguson JJ. NHLBI BARI clinical alert on diabetics treated with angioplasty. Circulation 1995;92:3371.
Portuese E, Orchard TJ. Mortality in insulin-dependent diabetes. In National Diabetes Data Group, editor. In Diabetes in America. 2 ed. Bethesda: National Institutes of Health; 1995. pp. 221–232.
Weintraub WS, Stein B, Kosinski A, Douglas JS Jr., Ghazzal ZM, Jones EL, et al. Outcome of coronary bypass surgery versus coronary angioplasty in diabetic patients with multivessel coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 1998;31:10–9.
Dorman JS, LaPorte RE, Kuller LH, Cruickshanks KJ, Orchard TJ, Wagener DK, et al. The Pittsburgh insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) morbidity and mortality study. Mortality results. Diabetes 1984;33:271–6.
Laing SP, Swerdlow AJ, Slater SD, Burden AC, Morris A, Waugh NR, et al. Mortality from heart disease in a cohort of 23,000 patients with insulin-treated diabetes. Diabetologia 2003;46:760–5.
Rodriguez BL, Fujimoto WY, Mayer-Davis EJ, Imperatore G, Williams DE, Bell RA, et al. Prevalence of cardiovascular disease risk factors in U.S. children and adolescents with diabetes: the SEARCH for diabetes in youth study. Diabetes Care 2006;29:1891–6.
Wadwa RP, Urbina EM, Dabelea D, Daniels SR, Snively BM, Ruggiero AM, et al. Diabetes type and duration are associated with increased arterial stiffness in the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study. Diabetes 2006;55:A2.
The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 1993;329:977–86.
Nathan DM, Cleary PA, Backlund JY, Genuth SM, Lachin JM, Orchard TJ, et al. Intensive diabetes treatment and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2005;353:2643–53.
Nathan DM, Lachin J, Cleary P, Orchard T, Brillon DJ, Backlund JY, et al. Intensive diabetes therapy and carotid intima-media thickness in type 1 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 2003;348:2294–303.
Snell-Bergeon JK, Hokanson JE, Jensen L, MacKenzie T, Kinney G, Dabelea D, et al. Progression of coronary artery calcification in type 1 diabetes: the importance of glycemic control. Diabetes Care 2003;26:2923–8.
Stettler C, Allemann S, Juni P, Cull CA, Holman RR, Egger M, et al. Glycemic control and macrovascular disease in types 1 and 2 diabetes mellitus: meta-analysis of randomized trials. Am Heart J 2006;152:27–38.
Krantz JS, Mack WJ, Hodis HN, Liu CR, Liu CH, Kaufman FR. Early onset of subclinical atherosclerosis in young persons with type 1 diabetes. J Pediatr 2004;145:452–7.
Haller MJ, Samyn M, Nichols WW, Brusko T, Wasserfall C, Schwartz RF, et al. Radial artery tonometry demonstrates arterial stiffness in children with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004;27:2911–7.
Silverstein J, Klingensmith G, Copeland K, Plotnick L, Kaufman F, Laffel L, et al. Care of children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes: a statement of the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2005;28:186–212.
Hansson L, Zanchetti A, Carruthers SG, Dahlof B, Elmfeldt D, Julius S, et al. Effects of intensive blood-pressure lowering and low-dose aspirin in patients with hypertension: principal results of the Hypertension Optimal Treatment (HOT) randomised trial. HOT Study Group. Lancet 1998;351:1755–62.
UK Prospective Diabetes Study Group. Tight blood pressure control and risk of macrovascular and microvascular complications in type 2ádiabetes: UKPDS 38. BMJ 1998;317:703–13.
Saydah SH, Fradkin J, Cowie CC. Poor control of risk factors for vascular disease among adults with previously diagnosed diabetes. JAMA 2004;291:335–42.
Maahs DM, Kinney GL, Wadwa P, Snell-Bergeon JK, Dabelea D, Hokanson J, et al. Hypertension prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control in an adult type 1 diabetes population and a comparable general population. Diabetes Care 2005;28:301–6.
National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 2004;114:555–76.
Schwab KO, Doerfer J, Hecker W, Grulich-Henn J, Wiemann D, Kordonouri O, et al. Spectrum and prevalence of atherogenic risk factors in 27,358 children, adolescents, and young adults with type 1 diabetes: cross-sectional data from the German diabetes documentation and quality management system (DPV). Diabetes Care 2006;29:218–25.
The Microalbuminuria Captopril Study Group. Captopril reduces the risk of nephropathy in IDDM patients with microalbuminuria. Diabetol 1996;39:587–93.
Chaturvedi N, Sjolie AK, Stephenson JM, Abrahamian H, Keipes M, Castellarin A, et al. Effect of lisinopril on progression of retinopathy in normotensive people with type 1 diabetes. The EUCLID Study Group. EURODIAB controlled trial of lisinopril in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Lancet 1998;351:28–31.
Arauz-Pacheco C, Parrott MA, Raskin P. The treatment of hypertension in adult patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care 2002;25:134–47.
Garg SK, Chase HP, Icaza G, Rothman RL, Osberg I, Carmain JA. 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure and renal disease in young subjects with type I diabetes. J Diabetes Complications 1997;11:263–7.
Lurbe E, Sorof JM, Daniels SR. Clinical and research aspects of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in children. J Pediatr 2004;144:7–16.
National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 2004;114:555–76.
Wadwa RP, Kinney GL, Maahs DM, Snell-Bergeon J, Hokanson JE, Garg SK, et al. Awareness and treatment of dyslipidemia in young adults with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2005;28:1051–6.
Weis U, Turner B, Gibney J, Watts GF, Burke V, Shaw KM, et al. Long-term predictors of coronary artery disease and mortality in type 1 diabetes. QJM 2001;94:623–30.
Colhoun HM, Otvos JD, Rubens MB, Taskinen MR, Underwood SR, Fuller JH. Lipoprotein subclasses and particle sizes and their relationship with coronary artery calcification in men and women with and without type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2002;51:1949–56.
Orchard TJ, Virella G, Forrest KY, Evans RW, Becker DJ, Lopes-Virella MF. Antibodies to oxidized LDL predict coronary artery disease in type 1 diabetes: a nested case–control study from the Pittsburgh epidemiology of diabetes complications study. Diabetes 1999;48:1454–8.
Kornerup K, Nordestgaard BG, Feldt-Rasmussen B, Borch-Johnsen K, Jensen KS, Jensen JS. Increased transvascular low density lipoprotein transport in insulin dependent diabetes: a mechanistic model for development of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2003;170:163–8.
Maahs DM, Maniatis AK, Nadeau K, Wadwa RP, McFann K, Klingensmith GJ. Total cholesterol and high-density lipoprotein levels in pediatric subjects with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Pediatr 2005;147:544–6.
Kershnar AK, Daniels SR, Imperatore G, Palla SL, Petitti DB, Pettitt DJ, et al. Lipid abnormalities are prevalent in youth with type 1 and type 2 diabetes: the search for diabetes in youth study. J Pediatr 2006;149:314–9.
American Diabetes Association. Management of dyslipidemia in children and adolescents with diabetes. Diabetes Care 2003;26:2194–7.
Rodenburg J, Vissers MN, Daniels SR, Wiegman A, Kastelein JJ. Lipid-lowering medications. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev 2004;2(Suppl 1):171–80.
de Jongh S, Ose L, Szamosi T, Gagne C, Lambert M, Scott R, et al. Efficacy and safety of statin therapy in children with familial hypercholesterolemia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with simvastatin. Circulation 2002;106:2231–7.
Lichtenstein AH, Appel LJ, Brands M, Carnethon M, Daniels S, Franch HA, et al. Diet and lifestyle recommendations revision 2006: a scientific statement from the American heart association nutrition committee. Circulation 2006;114:82–96.
Erbey JR, Kuller LH, Becker DJ, Orchard TJ. The association between a family history of type 2 diabetes and coronary artery disease in a type 1 diabetes population. Diabetes Care 1998;21:610–4.
Grundy SM, Balady GJ, Criqui MH, Fletcher G, Greenland P, Hiratzka LF, et al. Primary prevention of coronary heart disease: guidance from Framingham: a statement for healthcare professionals from the AHA task force on risk reduction. American heart association. Circulation 1998;97:1876–87.
Kavey RE, Daniels SR, Lauer RM, Atkins DL, Hayman LL, Taubert K. American Heart Association guidelines for primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease beginning in childhood. J Pediatr 2003;142:368–72.
Nicklas T, Johnson R. Position of the American dietetic association: dietary guidance for healthy children ages 2 to 11 years. J Am Diet Assoc 2004;104:660–77.
Mayer-Davis EJ, Nichols M, Liese AD, Bell RA, Dabelea DM, Johansen JM, et al. Dietary intake among youth with diabetes: the SEARCH for diabetes in youth study. J Am Diet Assoc 2006;106:689–97.
Riddell MC, Iscoe KE. Physical activity, sport, and pediatric diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes 2006;7:60–70.
Austin A, Warty V, Janosky J, Arslanian S. The relationship of physical fitness to lipid and lipoprotein(a) levels in adolescents with IDDM. Diabetes Care 1993;16:421–5.
Zieske AW, McMahan CA, McGill HC Jr., Homma S, Takei H, Malcom GT, et al. Smoking is associated with advanced coronary atherosclerosis in youth. Atherosclerosis 2005;180:87–92.
Haire-Joshu D, Glasgow RE, Tibbs TL. Smoking and diabetes. Diabetes Care 1999;22:1887–98.
American Diabetes Association. Smoking and Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004;27:74S–775S.
Hansson GK. Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med 2005;352:1685–95.
Libby P, Ridker PM, Maseri A. Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation 2002;105:1135–43.
Lindahl B, Toss H, Siegbahn A, Venge P, Wallentin L, The FRISC Study Group. Markers of myocardial damage and inflammation in relation to long-term mortality in unstable coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med 2000;343:1139–47.
Fisman EZ, Benderly M, Esper RJ, Behar S, Boyko V, Adler Y, et al. Interleukin-6 and the risk of future cardiovascular events in patients with angina pectoris and/or healed myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol 2006;98:14–8.
Zebrack JS, Anderson JL, Maycock CA, Horne BD, Bair TL, Muhlestein JB. Usefulness of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in predicting long-term risk of death or acute myocardial infarction in patients with unstable or stable angina pectoris or acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol 2002;89:145–9.
Maahs DM, Ogden LG, Kinney GL, Wadwa P, Snell-Bergeon JK, Dabelea D, et al. Low plasma adiponectin levels predict progression of coronary artery calcification. Circulation 2005;111:747–53.
Wadwa RP, Kinney GL, Ogden L, Snell-Bergeon JK, Maahs DM, Cornell E, et al. Soluble interleukin-2 receptor as a marker for progression of coronary artery calcification in type 1 diabetes. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2005.
Costacou T, Lopes-Virella MF, Zgibor JC, Virella G, Otvos J, Walsh M, et al. Markers of endothelial dysfunction in the prediction of coronary artery disease in type 1 diabetes. The Pittsburgh epidemiology of diabetes complications study. J Diabetes Complications 2005;19:183–93.
Gunczler P, Lanes R, Soros A, Verdu L, Ramon Y, Guevara B, et al. Coronary artery calcification, serum lipids, lipoproteins, and peripheral inflammatory markers in adolescents and young adults with type 1 diabetes. J Pediatr 2006;149:320–3.
Wadwa RP, Rewers M. Update on noninvasive detection of cardiovascular disease in diabetes. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes 2005;12:267–72.
Dabelea D, Kinney G, Snell-Bergeon JK, Hokanson JE, Eckel RH, Ehrlich J, et al. Effect of type 1 diabetes on the gender difference in coronary artery calcification: a role for insulin resistance? The coronary artery calcification in type 1 diabetes (CACTI) study. Diabetes 2003;52:2833–9.
Jarvisalo MJ, Raitakari M, Toikka JO, Putto-Laurila A, Rontu R, Laine S, et al. Endothelial dysfunction and increased arterial intima-media thickness in children with type 1 diabetes. Circulation 2004;109:1750–5.
Starkman HS, Cable G, Hala V, Hecht H, Donnelly CM. Delineation of prevalence and risk factors for early coronary artery disease by electron beam computed tomography in young adults with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2003;26:433–6.
UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 1998;352:837–53.
Battisti WP, Palmisano J, Keane WE. Dyslipidemia in patients with type 2 diabetes. relationships between lipids, kidney disease and cardiovascular disease. Clin Chem Lab Med 2003;41:1174–81.
Caro JJ, Ward AJ, O’Brien JA. Lifetime costs of complications resulting from type 2 diabetes in the U.S. Diabetes Care 2002;25:476–81.
Dabelea D, Maahs DM, Snively BM, Bell RA, Dolan LM, Hirsch IB, et al. High prevalence of elevated albumin excretion in youth with type 2 diabetes: the SEARCH for diabetes in youth study. Diabetol 2005;48:A53–4.
Eppens MC, Craig ME, Cusumano J, Hing S, Chan AKF, Howard NJ, et al. Prevalence of diabetes complications in adolescents with type 2 compared with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2006;29:1300–6.
Liu L, Hironaka K, Pihoker C. Type 2 diabetes in youth. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care 2004;34:254–72.
Steinberger J, Daniels SR. Obesity, insulin resistance, diabetes, and cardiovascular risk in children: an American heart association scientific statement from the atherosclerosis, hypertension, and obesity in the young committee (council on cardiovascular disease in the young) and the diabetes committee (council on nutrition, physical activity, and metabolism). Circulation 2003;107:1448–53.
Goran MI, Ball GDC, Cruz ML. Obesity and risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease in children and adolescents. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003;88:1417–27.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wadwa, R.P. Cardiovascular disease risk in youth with diabetes mellitus. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 7, 197–204 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11154-006-9016-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11154-006-9016-y