Abstract
Background
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is prevalent among patients with end-stage lung disease (ESLD). This disease can lead to microaspiration and may be a risk factor for lung damage before and after transplantation. A fundoplication is the best way to stop reflux, but little is known about the safety of elective antireflux surgery for patients with ESLD. This study aimed to report the safety of laparoscopic fundoplication for patients with ESLD and GERD before or after lung transplantation.
Methods
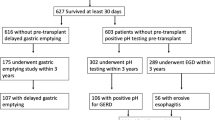
Between January 1997 and January 2007, 305 patients were listed for lung transplantation, and 189 patients underwent the procedure. In 2003, routine esophageal studies were added to the pretransplantation evaluation. After the authors’ initial experience, gastric emptying studies were added as well.
Results
A total of 35 patients with GERD or delayed gastric emptying were referred for surgical intervention. A laparoscopic fundoplication was performed for 32 patients (27 total and 5 partial). For three patients, a pyloroplasty also was performed. Two patients had a pyloroplasty without fundoplication. Of the 35 operations, 15 were performed before and 20 after transplantation. Gastric emptying of solids or liquids was delayed in 12 (92%) of 13 posttransplantation studies and 3 (60%) of 5 pretransplantation studies. All operations were completed laparoscopically, and 33 patients recovered uneventfully (94%). The median hospital length of stay was 2 days (range, 1–34 days) for the patients admitted to undergo elective operations. Hospitalization was not prolonged for the three patients who had fundoplications immediately after transplantation.
Conclusions
The results of this study show that laparoscopic antireflux surgery can be performed safely by an experienced multidisciplinary team for selected patients with ESLD before or after lung transplantation, and that gastric emptying is frequently abnormal and should be objectively measured in ESLD patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tobin RW, Pope CE, Pellegrini CA, Emond MJ, Sillery J, Raghu G (1998) Increased prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 158:1804–1808
Cantu E, Appel JZ, Hartwig MG, Woreta H, Green C, Messier R, Palmer SM, Davis RD Jr. (2004) Early fundoplication prevents chronic allograft dysfunction in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. J. Maxwell Chamberlain Memorial Paper. Ann Thorac Surg 78:1142–1151, discussion 1142–1151
D’Ovidio F, Singer LG, Hadjiliadis D, Pierre A, Waddell TK, de Perrot M, Hutcheon M, Miller L, Darling G, Keshavjee S (2005) Prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux in end-stage lung disease candidates for lung transplant. Ann Thorac Surg 80:1254–1260
Raghu G, Freudenberger TD, Yang S, Curtis JR, Spada C, Hayes J, Sillery JK, Pope CE, Pellegrini CA (2006) High prevalence of abnormal acid gastro-oesophageal reflux in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir J 27:136–142
Sweet MP, Herbella FA, Leard L, Hoopes C, Golden J, Hays S, Patti MG (2006) The prevalence of distal and proximal gastroesophageal reflux in patients awaiting lung transplantation. Ann Surg 244:491–497
D’Ovidio F, Mura M, Ridsdale R, Takahashi H, Waddell TK, Hutcheon M, Hadjiliadis D, Singer LG, Pierre A, Chaparro C, Gutierrez C, Miller L, Darling G, Liu M, Post M, Keshavjee S (2006) The effect of reflux and bile acid aspiration on the lung allograft and its surfactant and innate immunity molecules SP-A and SP-D. Am J Transplant 6:1930–1938
Berkowitz N, Schulman LL, McGregor C, Markowitz D (1995) Gastroparesis after lung transplantation: potential role in postoperative respiratory complications. Chest 108:1602–1607
Bodet-Milin C, Querellou S, Oudoux A, Haloun A, Horeau-Llanglard D, Carlier T, Bizais Y, Couturier O (2006) Delayed gastric emptying scintigraphy in cystic fibrosis patients before and after lung transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 25:1077–1083
D’Ovidio F, Keshavjee S (2006) Gastroesophageal reflux and lung transplantation. Dis Esophagus 19:315–320
Linden PA, Gilbert RJ, Yeap BY, Boyle K, Deykin A, Jaklitsch M, Sugarbaker DJ, Bueno R (2006) Laparoscopic fundoplication in patients with end-stage lung disease awaiting transplantation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 131:438–446
Farrell TM, Richardson WS, Halkar R, Lyon CP, Galloway KD, Waring JP, Smith CD, Hunter JG (2001) Nissen fundoplication improves gastric motility in patients with delayed gastric emptying. Surg Endosc 15:271–274
Patti MG, Fisichella PM, Perretta S (2001) Preoperative evaluation of patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 11:327–331
Jamieson JR, Stein HJ, DeMeester TR, Bonavina L, Schwizer W, Hinder RA, Albertucci M (1992) Ambulatory 24-h esophageal pH monitoring: normal values, optimal thresholds, specificity, sensitivity, and reproducibility. Am J Gastroenterol 87:1102–1111
Tedesco P, Lobo E, Fisichella PM, Way LW, Patti MG (2006) Laparoscopic fundoplication in elderly patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Arch Surg 141:289–292, discussion 292
Hartwig MG, Appel JZ, Davis RD (2005) Antireflux surgery in the setting of lung transplantation: strategies for treating gastroesophageal reflux disease in a high-risk population. Thorac Surg Clin 15:417–427
Tamhankar AP, Peters JH, Portale G, Hsieh CC, Hagen JA, Bremner CG, DeMeester TR (2004) Omeprazole does not reduce gastroesophageal reflux: new insights using multichannel intraluminal impedance technology. J Gastrointest Surg 8:890–897, discussion 897–898
Herbella FA, Tedesco P, Nipomnick I, Fisichella PM, Patti MG (2007) Effect of partial and total laparoscopic fundoplication on esophageal body motility. Surg Endosc 21:285–288
Acknowledgments
W. Gasper was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health (5T32 DK07573–18).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Presented as a Poster of Distinction at the Spring 2007 Meeting of the Society of Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES) at Las Vegas, Nevada, 18–22 April 2007
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gasper, W.J., Sweet, M.P., Hoopes, C. et al. Antireflux surgery for patients with end-stage lung disease before and after lung transplantation. Surg Endosc 22, 495–500 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-007-9494-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-007-9494-3