Abstract.
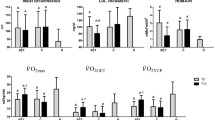
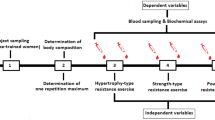
This study examined the effects of 6 months of resistance exercise (RX) on basal and post-aerobic exercise lipid peroxidation (LIPOX). Men and women [n=62, mean (SD) age 68.4 (6) years] were divided randomly into either a control (n=16, CON), low-intensity training [LEX n=24; 50% one-repetition maximum (1RM), 13 repetitions/exercise], or high-intensity training (HEX n=22, 80% 1RM, 8 repetitions/exercise) group. Pre- and post-training, subjects performed a graded aerobic exercise test (GXT). Blood samples were collected prior to and 10 min following each GXT. Subjects trained 3 times per week for 6 months using 12 RX machines. LIPOX was determined by measuring levels of thiobarbituric reactive acid substances (TBARS) and lipid hydroperoxides (PEROX). RX had no effect on resting LIPOX. Post-training, post-GXT TBARS were lower in the LEX and HEX groups by 14% and 18%, respectively, compared to CON (P<0.05). Post-GXT PEROX levels were lower (P<0.05) in LEX and HEX compared to CON [CON 3.51 (0.56) nmol/ml, LEX 2.89 (0.80) nmol/ml, HEX 2.99 (0.63) nmol/ml]. Serum total and non-protein (glutathione) thiols were higher in the LEX and HEX groups following training compared to CON (P<0.05). These data suggest that RX can (1) reduce serum LIPOX, (2) provide protection against oxidizing agents in vitro, and (3) provide a "cross-protection" against the oxidative stress generated by aerobic exercise, perhaps mediated by improvements in the thiol portion of the antioxidant defense.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vincent, K.R., Vincent, H.K., Braith, R.W. et al. Resistance exercise training attenuates exercise-induced lipid peroxidation in the elderly. Eur J Appl Physiol 87, 416–423 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-002-0640-2
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-002-0640-2