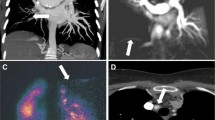
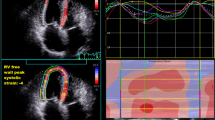
Abstract
In the recent World Health Organization (WHO) classification the group of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PH) comprises the classic primary pulmonary hypertension and several conditions with definite or very high risk factors to develop pulmonary arterial hypertension. Therapeutic advances drive the need for a comprehensive pre-therapeutic evaluation for optimal treatment. Furthermore, follow-up examinations need to be performed to monitor changes in disease status and response to therapy. Up to now, the diagnostic imaging work-up of PH comprises mainly echocardiography, invasive right heart catheterization and ventilation/perfusion scintigraphy. Due to technical advances helical computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) became more important in the evaluation and for differential diagnosis of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Both modalities are reviewed and recommendations for clinical use are given.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fowler NO, Wescott RN, Scott RC (1953) Normal pressure in right heart and pulmonary artery. Am Heart J 46:264–270
Chatterjee K, De Marco T, Alpert JS (2002) Pulmonary hypertension: hemodynamic diagnosis and management. Arch Int Med 162:1925–1933
Davidson WR, Fee EC (1990) Influence of aging on pulmonary hemodynamics in a population free of coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol 65:1454–1458
Nauser TD, Stites SW (2001) Diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Am Fam Physician 63:1789–1798
McLaughlin VV (2002) Primary pulmonary hypertension. Hospital Physician Board Review Manual 9:1–11
Kubo N, Tomita H, Fuse S, Abe N, Hatakeyama K, Chiba S (2001) Helical computer assisted tomography in pulmonary hypertension complicating left-to-right shunts–correlation with pulmonary hemodynamics. Jpn Circ J 65:188–92
Gluecker T, Capasso P, Schnyder P, Gudinchet F, Schaller MD, Revelly JP, Chiolero R, Vock P, Wicky S (1999) Clinical and radiologic features of pulmonary edema. Radiographics 19:1507–1531; discussion 1532–1533
Resten A, Maitre S, Humbert M, Sitbon O, Capron F, Simoneau G, Musset D (2002) Pulmonary arterial hypertension: thin-section CT predictors of epoprostenol therapy failure. Radiology 222:782–788
Chung MH, Edinburgh KJ, Webb EM, McCowin M, Webb WR (2001) Mixed infiltrative and obstructive disease on high-resolution CT: differential diagnosis and functional correlates in a consecutive series. J Thorac Imaging 16:69–75
Fraser KL, Tullis DE, Sasson Z, Hyland RH, Thornley KS, Hanly PJ (1999) Pulmonary hypertension and cardiac function in adult cystic fibrosis: role of hypoxemia. Chest 115:1321–1328
Roberts HC, Kauczor H-U, Schweden F, Thelen M (1997) Spiral CT of pulmonary hypertension and chronic thromboembolism. J Thorac Imaging 12:118–127
Schwickert HC, Schweden F, Schild HH, Piepenburg R, Düber C, Kauczor H-U, Renner C, Iversen S, Thelen M (1994) Pulmonary arteries and lung parenchyma in chronic pulmonary embolism: preoperative and postoperative CT findings. Radiology 191:351–357
Hansell DM (1999) High-resolution computed tomography in the evaluation of fibrosing alveolitis. Clin Chest Med 20:739–760, viii
Kauczor H-U, Kreitner K-F (1999) MRI of the pulmonary parenchyma. Eur Radiol 9:1755–1764
Mayo JR, MacKay A, Muller NL (1992) MR imaging of the lungs: value of short TE spin-echo pulse sequences. AJR Am J Roentgenol 159:951–956
Knopp MV, Hess T, Schad LR, Bischoff HG, Weisser G, Blüml S, van Kaick G (1994) MR tomography of lung metastases with rapid gradient echo sequences. Initial results in diagnostic applications. Radiologe 34:581–587
Hatabu H, Gaa J, Tadamura E, Edinburgh KJ, Stock KW, Garpestad E, Edelman RR (1999) MR imaging of pulmonary parenchyma with a half-Fourier single-shot turbo spin-echo (HASTE) sequence. Eur J Radiol 29:152–159
Rupprecht T, Bowing B, Kuth R, Deimling M, Rascher W, Wagner M (2002) Steady-state free precession projection MRI as a potential alternative to the conventional chest X-ray in pediatric patients with suspected pneumonia. Eur Radiol 12:2752–2756
Heussel CP, Sandner A, Voigtlander T, Heike M, Deimling M, Kuth R, Rupprecht T, Schreiber WG, Kauczor HU (2002) Prospective feasibility study of chest X-ray vs thoracic MRI in breath-hold technique at an open low-field scanner. Fortschr Röntgenstr 174:854–861
Biederer J, Busse I, Grimm J, Reuter M, Muhle C, Freitag S, Heller M (2002) Sensitivity of MRI in detecting alveolar Infiltrates: experimental studies. Fortschr Röntgenstr 174:1033–1039
Donnelly LF, MacFall JR, McAdams HP, Majure JM, Smith J, Frush DP, Bogonad P, Charles HC, Ravin CE (1999) Cystic fibrosis: combined hyperpolarized 3He-enhanced and conventional proton MR imaging in the lung–preliminary observations. Radiology 212:885–889
Biederer J, Both M, Graessner J, Liess C, Jakob P, Reuter M, Heller M (2003) Lung morphology: fast MR imaging assessment with a volumetric interpolated breath-hold technique: initial experience with patients. Radiology 226:242–249
Griswold MA, Jakob PM, Heidemann RM, Nittka M, Jellus V, Wang J, Kiefer B, Haase A (2002) Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA). Magn Reson Med 47:1202–1210
Perloff JK, Hart EM, Greaves SM, Miner PD, Child JS (2003) Proximal pulmonary arterial and intrapulmonary radiologic features of Eisenmenger syndrome and primary pulmonary hypertension. Am J Cardiol 92:182–187
Gulsun M, Goodman LR (2003) CT for the diagnosis of venous thromboembolic disease. Curr Opin Pulm Med 9:367–373
Bugnone AN, Viamonte M Jr, Garcia H (2002) Imaging findings in human immunodeficiency virus-related pulmonary hypertension: report of five cases and review of the literature. Radiology 223:820–827
Lawler LP, Corl FM, Fishman EK (2002) Multi-detector row and volume-rendered CT of the normal and accessory flow pathways of the thoracic systemic and pulmonary veins. Radiographics 22 Spec No:S45–S60
Kuriyama K, Gamsu G, Stern RG, Cann CE, Herfkens RJ, Brundage BH (1984) CT-determined pulmonary artery diameters in predicting pulmonary hypertension. Invest Radiol 19:16–22
Remy-Jardin M, Mastora I, Remy J (2003) Pulmonary embolus imaging with multislice CT. Radiol Clin North Am 41:507–519
McGoon MD (2001) The assessment of pulmonary hypertension. Clin Chest Med 22:493–508
Williamson TL, Kim NH, Rubin LJ (2002) Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 45:203–212
Hagl C, Khaladj N, Peters T, Hoeper MM, Logemann F, Haverich A, Macchiarini P (2003) Technical advances of pulmonary thromboendarterectomy for chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 23:776–781
Vogt FM, Goyen M, Debatin JF (2003) MR angiography of the chest. Radiol Clin North Am 41:29–41
Ohno Y, Kawamitsu H, Higashino T, Takenaka D, Watanabe H, van Cauteren M, Fujii M, Hatabu H, Sugimura K (2003) Time-resolved contrast-enhanced pulmonary MR angiography using sensitivity encoding (SENSE). J Magn Reson Imaging 17:330–336
Oudkerk M, van Beek EJ, Wielopolski P, van Ooijen PM, Brouwers-Kuyper EM, Bongaerts AH, Berghout A (2002) Comparison of contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography and conventional pulmonary angiography for the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism: a prospective study. Lancet 359:1643–1647
Kreitner K-F, Ley S, Kauczor H-U, Kalden P, Pitton MB, Mayer E, Laub G, Thelen M (2000) Assessment of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension by three-dimensional contrast-enhanced MR angiography– comparison with selective intraarterial DSA. Fortschr Röntgenstr 172:1–6
Ley S, Kauczor HU, Heussel CP, Kramm T, Mayer E, Thelen M, Kreitner KF (2003) Value of contrast-enhanced MR angiography and helical CT angiography in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Eur Radiol 13:2365–2371
Shimoda LA, Sham JS, Sylvester JT (2000) Altered pulmonary vasoreactivity in the chronically hypoxic lung. Physiol Res 49:549–560
Cleverley JR, Desai SR, Wells AU, Koyama H, et al (2000) Evaluation of patients undergoing lung volume reduction surgery: ancillary information available from computed tomography. Clin Radiol 55:45–50
Groell R, Peichel KH, Uggowitzer MM, Schmid F, Hartwagner K (1999) Computed tomography densiometry of the lung: a method to assess perfusion defects in acute pulmonary embolism. Eur J Radiol 32:192–196
Wildberger JE, Niethammer MU, Klotz E, Schaller S, Wein BB, Günther RW (2001) Multi-slice CT for visualization of pulmonary embolism using perfusion weighted color maps. Fortschr Röntgenstr 173:289–294
Schoepf UJ, Kessler MA, Rieger C, Bohme E, Schaller S, Ohnesorge BM, Niethammer M, Becker CR, Reiser MF (2001) Diagnosis of pulmonary embolism with multislice spiral CT. Radiologe 41:248–255
Schoepf UJ, Bruening R, Konschitzky H, Becker CR, Knez A, Weber J, Muehling O, Herzog P, Huber A, Haberl R, Reiser MF (2000) Pulmonary embolism: comprehensive diagnosis by using electron-beam CT for detection of emboli and assessment of pulmonary blood flow. Radiology 217:693–700
Uematsu H, Ohno Y, Hatabu H (2003) Recent advances in magnetic resonance perfusion imaging of the lung. Top Magn Reson Imaging 14:245–251
Keilholz SD, Mai VM, Berr SS, Fujiwara N, Hagspiel KD (2002) Comparison of first-pass Gd-DOTA and FAIRER MR perfusion imaging in a rabbit model of pulmonary embolism. J Magn Reson Imaging 16:168–171
Uematsu H, Levin DL, Hatabu H (2001) Quantification of pulmonary perfusion with MR imaging: recent advances. Eur J Radiol 37:155–163
Amundsen T, Torheim G, Kvistad KA, Waage A, Bjermer L, Nordlid KK, Johnsen H, Asberg A, Haraldseth O (2002) Perfusion abnormalities in pulmonary embolism studied with perfusion MRI and ventilation-perfusion scintigraphy: an intra-modality and inter-modality agreement study. J Magn Reson Imaging 15:386–394
Nakagawa T, Sakuma H, Murashima S, Ishida N, Matsumura K, Takeda K (2001) Pulmonary ventilation-perfusion MR imaging in clinical patients. J Magn Reson Imaging 14:419–424
Fink C, Bock M, Puderbach M, Schmähl A, Delorme S (2003) Partially parallel three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of lung perfusion—initial results. Invest Radiol 38:482–488
Baile EM, Ling H, Heyworth JR, Hogg JC, Pare PD (1985) Bronchopulmonary anastomotic and noncoronary collateral blood flow in humans during cardiopulmonary bypass. Chest 87:749–754
Kuhlmann U, Lanser K (1988) Die Bedeutung der Bronchialzirkulation bei pulmonaler Hypertonie. Internist 29:664–670
Kauczor H-U, Schwickert HC, Mayer E, Schweden F, Schild HH, Thelen M (1994) Spiral CT of bronchial arteries in chronic thromboembolism. J Comput Assist Tomogr 18:855–861
Robertson HT, Jindal SK, Lakshminarayan S, Albert R, Kirk W, Hlastala MP, Butler J (1984) Gas exchange properties of the bronchial circulation in a dog lobe maintained in zone 1 conditions. Am Rev Respir Dis 129:A229
Murayama S, Hashiguchi N, Murakami J, Sakai S, Matsumoto S, Mizushima A, Hasuo K, Masuda K (1996) Helical CT imaging of bronchial arteries with curved reformation technique in comparison with selective bronchial arteriography: preliminary report. J Comput Assist Tomogr 20:749–755
Ley S, Kreitner K-F, Morgenstern I, Thelen M, Kauczor H-U (2002) Bronchopulmonary shunts in patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: evaluation by helical CT and MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 179:1209–1215
Caso P, Galderisi M, Cicala S, Cioppa C, D’Andrea A, Lagioia G, Liccardo B, Martiniello AR, Mininni N (2001) Association between myocardial right ventricular relaxation time and pulmonary arterial pressure in chronic obstructive lung disease: analysis by pulsed Doppler tissue imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 14:970–977
Nakamura K, Miyahara Y, Ikeda S, Naito T (1995) Assessment of right ventricular diastolic function by pulsed Doppler echocardiography in chronic pulmonary disease and pulmonary thromboembolism. Respiration 62:237–243
Vizza CD, Lynch JP, Ochoa LL, Richardson G, Trulock EP (1998) Right and left ventricular dysfunction in patients with severe pulmonary disease. Chest 113:576–583
Arcasoy SM, Christie JD, Ferrari VA, Sutton MS, Zisman DA, Blumenthal NP, Pochettino A, Kotloff RM (2003) Echocardiographic assessment of pulmonary hypertension in patients with advanced lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 167:735–740
Carrascosa PM, Capunay CM, Parodi JC, Padilla LT, Johnson P, Carrascosa JM, Chandra S, Smith D, Belardi J (2003) General utilities of multislice tomography in the cardiac field. Herz 28:44–51
Wintersperger BJ, Stäbler A, Seemann M, Holzknecht N, Helmberger T, Fink U, Reiser MF (1999) Evaluation of right ventricular performance in patients with acute pulmonary embolism by helical CT. Fortschr Röntgenstr 170:542–549
Halliburton SS, Petersilka M, Schvartzman PR, Obuchowski N, White RD (2003) Evaluation of left ventricular dysfunction using multiphasic reconstructions of coronary multi-slice computed tomography data in patients with chronic ischemic heart disease: validation against cine magnetic resonance imaging. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 19:73–83
Contractor S, Maldjian PD, Sharma VK, Gor DM (2002) Role of helical CT in detecting right ventricular dysfunction secondary to acute pulmonary embolism. J Comput Assist Tomogr 26:587–591
Trabold T, Buchgeister M, Kuttner A, Heuschmid M, Kopp AF, Schroder S, Claussen CD (2003) Estimation of radiation exposure in 16-detector row computed tomography of the heart with retrospective ECG-gating. Fortschr Röntgenstr 175:1051–1055
Chatzimavroudis GP, Oshinski JN, Franch RH, Walker PG, Yoganathan AP, Pettigrew RI (2001) Evaluation of the precision of magnetic resonance phase velocity mapping for blood flow measurements. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 3:11–19
Pattynama PMT, Lamb HJ, van der Velde EA, van der Geest RJ, van der Wall EE, de Roos A (1995) Reproducibilty of MRI-derived measurements of right ventricular volumes and myocardial mass. J Magn Reson Imaging 13:53–63
Rominger MB, Bachmann GF, Pabst W, Rau WS (1999) Right ventricular volumes and ejection fraction with fast cine MR imaging in breath-hold technique: applicability, normal values from 52 volunteers, and evaluation of 325 adult cardiac patients. J Magn Reson Imaging 10:908–918
Alfakih K, Plein S, Thiele H, Jones T, Ridgway JP, Sivananthan MU (2003) Normal human left and right ventricular dimensions for MRI as assessed by turbo gradient echo and steady-state free precession imaging sequences. J Magn Reson Imaging 17:323–329
Lotz J, Meier C, Leppert A, Galanski M (2002) Cardiovascular flow measurement with phase-contrast MR imaging: basic facts and implementation. Radiographics 22:651–671
Rominger MB, Dinkel HP, Bachmann GF (2002) Comparison between fast MR flow quantification in breathhold technique in ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk with right and left ventricular cine-MRI for the assessment of stroke volumes in healthy volunteers. Fortschr Röntgenstr 174:196–201
Laffon E, Laurent F, Bernard V, De Boucaud L, Ducassou D, Marthan R (2001) Noninvasive assessment of pulmonary arterial hypertension by MR phase-mapping method. J Appl Physiol 90:2197–2202
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the German Research Council (DFG, FOR 474).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ley, S., Kreitner, KF., Fink, C. et al. Assessment of pulmonary hypertension by CT and MR imaging. Eur Radiol 14, 359–368 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-003-2208-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-003-2208-x