Abstract.
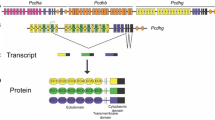
Phylogenetic analysis of protocadherin genes identified a new gene subfamily, the δ-protocadherins, containing several conserved motifs in their cytoplasmic domains. This subfamily can be further subdivided into two subgroups, named δ1-protocadherins (comprising protocadherin-1, -7, -9, and -11 or X/Y) and δ2-protocadherins (comprising protocadherin-8, -10, -17, -18, and -19). The members of the δ1-protocadherin subgroup were analyzed in greater detail here. They share a similar gene structure that results in the expression of multiple alternative transcripts. All members of this subgroup have at least one transcript that contains a binding site for protein phosphatase-1α. Like most classic cadherins, each of three δ1-protocadherins analyzed in this study by in situ hybridization showed a unique expression pattern that differed from the patterns of the other δ1-protocadherins. Together, these results suggest that the members of the δ1-protocadherin subgroup exercise tightly regulated functions in the development, regionalization, and functional differentiation of the mouse brain.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 14 January 2005; received after revision 24 February 2005; accepted 18 March 2005
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vanhalst, K., Kools, P., Staes, K. et al. δ-Protocadherins: a gene family expressed differentially in the mouse brain. CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 62, 1247–1259 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-005-5021-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-005-5021-7